In this Article
The Philippines continues to face significant challenges in pursuing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), as many of the advancements achieved in recent years have been undermined by the effects of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic.

According to the Current Status Index (CSI), progress was observed in Goal 1 (No Poverty), Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-Being), Goal 4 (Quality Education), and Goal 14 (Life Below Water) since 2000; however, it remains below the expected progress for 2022. On the other hand, Goal 2 (Zero Hunger), Goal 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth), Goal 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities), and Goal 13 (Climate Action) have declined since 2000. Notably, of all the goals, only Goal 17 (Partnerships for the Goals) has exceeded the 2022 benchmark, though this achievement is based on just one of the 13 indicators within the goal, which may not provide a comprehensive assessment of the overall progress for Goal 17.
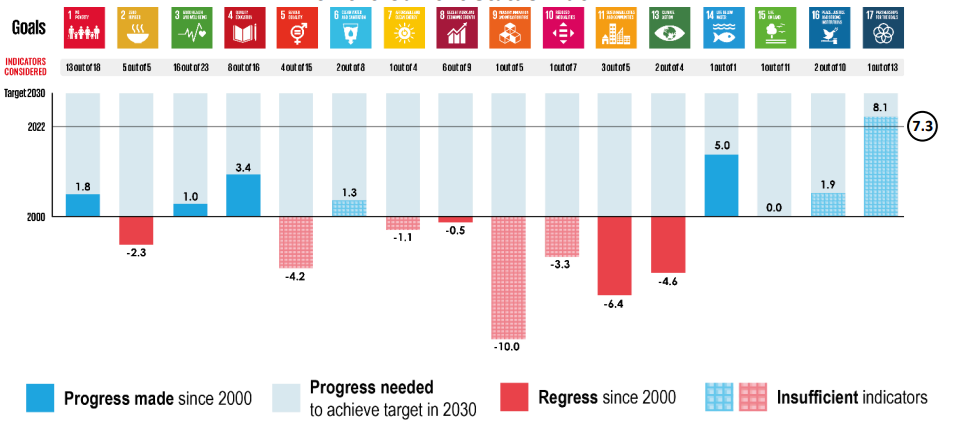
CSI is a measure developed by the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP) that assesses the current stage of progress by creating a linkage between the progress made since the baseline and the progress needed by 2030. It requires at least two data points since 2000 and the 2030 numerical target. It provides progress at the goal level.
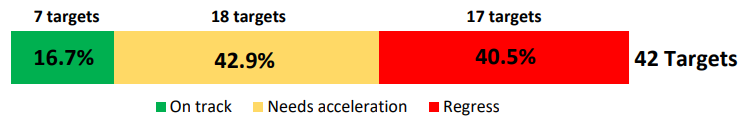
Meanwhile, the Anticipated Progress Index measures how much extra effort is needed to meet the target by 2030, assuming the pace of progress is sustained. It requires at least three data points since 2000 and the 2030 numerical target. It provides progress at the target and indicator levels.
The Anticipated Progress Index revealed that 16.7 percent of the targets with measurable progress are on track. However, 42.9 percent require accelerated efforts to achieve the desired outcomes. In comparison, the remaining 40.5 percent of SDG targets necessitate an exponential increase in progress to reverse the downtrend and meet the 2030 goals.
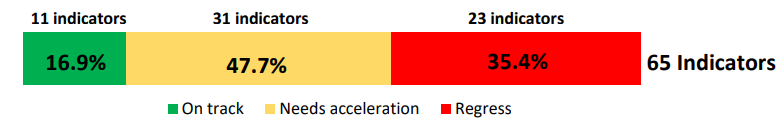
Similarly to the SDG target level, 16.9 percent of those meeting data requirements are on track, while nearly half (47.7 percent) of indicators with measurable progress require acceleration. Meanwhile, 35.4 percent need a reversal in current trends to achieve the targets.
Reference: Philippine Statistics Authority. (14, June 2023). Progress on the Philippine Sustainable Development Goals based on the SDG Watch posted on 27 January 2023. Retrieved October 30, 2024, from https://psa.gov.ph/system/files/phdsd/Press%20Release_2022%202nd%20round%20Pace%20of%20Progress_14June2023_1.pdf




