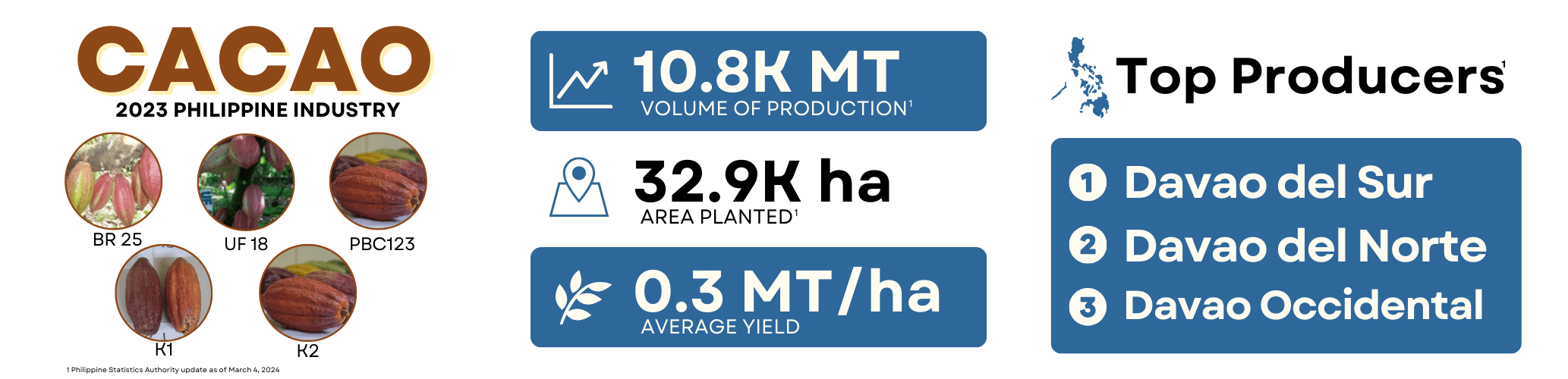
Cacao
Industry Strategic Science and Technology Program
Cacao Industry Profile
Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.) tagged as “food of the gods” is a perennial crop that has a great potential market value in the world. It is grown for its beans, which are processed into tablea, cocoa powder, nibs, butter, paste/liquor and chocolate confectionery. These products gained popularity not only in the chocolate industry but also in cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries. Cacao production is labor intensive, which is primarily produced by hand thereby making it an important source of livelihoods. Cocoa-chocolate industry is a multi-million-dollar industry that connects cocoa bean producers with manufacturers and consumers of chocolate. The growing demand on cacao and chocolate products both in the international and local market presents its promising contribution to the country’s economic development.
Globally, cocoa farmers produce around five million tons of cocoa beans per year. Of the total production, 70% comes from Africa (mainly from West Africa), 19% from Asia and Oceania and 11% from the Americas. The biggest cocoa-growing countries are Côte d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) and Ghana, accounting for more than half of the worldwide cocoa production. More than a third of the cocoa beans are processed in Europe (Swiss Platform for Sustainable Cacao, 2021). According to the World Cocoa Foundation (WCF) there are 5-6 million cocoa farmers worldwide, and the number of people who depend upon cacao for their livelihood is 40-50 million.
Problems in the Industry
The Philippines is one of the countries in Asia seen to have a competitive advantage for cacao production due to its strategic location, good climatic condition, and favorable soil. However, despite its competitive advantage, cacao production in the country is still unable to meet the current requirements of the growing cacao-based industry due to several problems affecting the industry, and thus resort to importing cacao beans from other producing countries. Some of the identified impediments to cacao production in the country include:
- Low productivity level, less than 2kg/tree/tree;
- Inadequate skills of cacao farmers and/or inappropriate technology used due to varying technologies and protocols introduced;
- Limitation on the government extension services/technology transfer on cacao production;
- Production Issues: Area suitability, low organic matter, climate change, absence of mitigating measures against typhoon/flood and prevalence of pest and diseases; Clonal compatibility, too much use of plastic sleeves, etc;
- Low Quality of Beans: Inadequate skills on post-harvest and bean grading, limited access to post harvest facilities and low level of awareness on quality & standards;
- High cost of production inputs particularly fertilizer, pesticide
- Inadequate Farm-to-market Roads (FMR), logistics;
- Inconsistent/inaccurate industry production database.
Cacao Policies
| Policy Type | Policy Number | Policy Year | Congress | Policy Title | Policy Description | Policy Objective | Policy Link | Commodity | Classification | info_encoder_stamp | info_date_stamp | info_quashing_remarks | filepath |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bill | House Bill No. 1411 | 2022 | 19th | An Act Institutionalizing a National Cacao Development Program, Creating for the Purpose the Philippine Cacao Council, Appropriating Funds Therefor, and For Other Purposes | It is hereby declared the policy of the State to develop a sustainable and competitive cacao industry that is environmentally sound, economically viable, socially responsive and aimed to spur development through livelihood creation, job generation, and income augmentation thereby contributing to poverty alleviation, inclusive growth,and peace and order attainment particularly in the rural areas. | This bill envisions the creation of a national program, which seeks to gather government agencies together with the Department of Agriculture as lead agency to do education training of all stakeholders in the cacao industry, collecting relevant researches, scientiifc studies, and market strategies, extending technologies and creating international linkages for development, promotion and be a competitor in the world cacao market. | https://hrep-website.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/legisdocs/basic_19/HB01411.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6591 | 2022 | 19th | An Act Creating the National Cacao Authority to Accelerate the Development of the Cacao Industry in the Philippines, Providing for a Cacao Development Fund, and For Other Purposes | The Cacao Industry in the Philippines desperately needs national government intervention to assure its stability and development. Despite being ideal for cacao plantationa dn production, the country has not been on par with other leading ASEAN countries like Indonesia and Malaysia who are continually on the top of cocoa bean production. It is high time for the Philippines to step up its productivity in cacao and cocoa products to not only reach the national demand but also work its way up to not only among the top ASEAN countries in terms of cacao and cocoa production, as well as among the top in the world. | The bill seeks to establish the National Cacao Authority as the legal body and leading agency for the further development of the cacao industry in the country and other matters theof. The establishment of the Authority would also give our local farmers the opportunity to enter the cacao market and/or industry with the help of the national government. | https://hrep-website.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06591.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | Senate Bill No. 1387 | 2022 | 19th | An Act Creating A Cacao Research And Development Center, Authorizing The Appropriation Of Funds Therefor, And For Other Purposes | The Center shall have the following general powers and functions in line with the research and development programs of the Department of Agriculture - Bureau of Agricultural, Research (DA-BAR), Department of Science and Technology (DOST), Department of Trade and Industry (DTI), and National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA): a. Educate and train all stakeholders of the cacao industry; b. Conduct relevant research, scientific study, and feasible marketing strategies; c. Extend technologies; and d. Establish linkages with international organizations and other cacao development centers in other countries. | The legislation envisions the creation of a center that will have general powers and functions in line with the research and development of the Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Agricultural Research (OA-BAR), Department of Science and Technology (DOST), Department of Trade and Industry (DTI), and the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA). | https://legacy.senate.gov.ph/lisdata/3965435970!.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 1370 House Bill No. 3546 | 2022 | 19th | An Act Establishing A National Program For The Cacao Industry And Appropriating Funds Therefor | It is hereby declared the policy of the State to develop a sustainable cacao industry that optimizes local production capacity, the application of sustainable agriculture practices, secures quality raw materials and their processing, provides marketing of cacao beans in its raw or processed form, and participates in the international cacao trade for the economic relief of smallholder farmers. There is also hereby created the National Cacao Development Council (NCDC), under the Department of Agriculture, which shall formulate the cacao development plan, educate and train all stakeholders of the cacao industry, and conduct relevant research, scientific study and feasible marketing strategies, among others. | The bill seeks to implement a national program for the education and training of stakeholders in the cacao industry, collect relevant research, scientific studies and market strategies for the proliferation of the local cacao industry. It envisions the various government agencies together with the Department of Agriculture (DA), as lead agency, in this endeavor of making the Philippines a competitor in the world cacao market. | https://hrep-website.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/legisdocs/basic_19/HB01370.pdf https://hrep-website.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/legisdocs/basic_19/HB03546.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 2931 | 2022 | 19th | An Act Developing The Cacao Industry In Cagayan Valley Region, Creating For The Purpose The Cacao Subsidy Fund And The Cacao Research And Development Center And Appropriating Funds Therefor | There shall be created the Cacao Research and Development Center in Cagayan which shall be attached to the Cagayan State University. The Cacao Research and Development Center shall undertake and conduct researches and technical studies on the development, production, management and marketing of cacao and its by-products, and provide technical assistance and support to cacao farmers and producers and other stakeholders in the Cagayan Valley Region, among others. There is also hereby created a Cacao Subsidy Fund, which shall be used to financially support the Cacao industry. | The bill aims to promote, enhance, protect, and increase cacao production in the Cagayan Valley region by providing ample technical and financial support to the local farmers to further improve the production quality of its products to be at par with the internationally traded ones. | https://hrep-website.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/legisdocs/basic_19/HB02931.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Law | Republic Act No. 11547 | 2021 | 18th | An Act Declaring The City Of Davao As The Chocolate Capital Of The Philippines And The Entire Region X1 (Davao Region) As The Cacao Capital Of The Philippines | The law recognizes the significant contributions of cacao in establishing the country's reputation for producing high-quality chocolate beans, as well as providing livelihood opportunities to numerous small-scale farmers in rural areas. | The Act aims to recognize and declare Davao CIty as the Cacao and Chocolate Capital of the Philippines. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/downloads/2021/05may/20210527-RA-11547-RRD.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | Senate Bill No. 1741 | 2020 | 18th | An Act Declaring The City Of Davao As The Cacao And Chocolate Capital Of The Philippines | In recognition of the status as the country's biggest producer of cacao and its vital contribution in making the Philippines world renowned and sought after by chocolate makers from the U.S., Japan, and Europe, the City of Davao is hereby declared the Cacao and Chocolate Capital of the Philippines. | The bill aims to recognize and declare Davao as the Cacao and Chocolate Capital of the Philippines. | http://legacy.senate.gov.ph/lisdata/3330530141!.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Joint Memorandum Order | Joint Memorandum Order No. 01 | 2020 | null | Establishing the National Convergence Initiative for Sustainable Rural Development (NCI-SRD) Coordination Mechanism for Rubber, Fiber Crops, Coffee, Cacao, and Other High Value Crops | This Order shall include the following: Major programs of the NCI-SRD agencies involving rubber, fiber crops, coffee, cacao, and other high value crops but not limited to: 1. DA High Value Crops Development Program (HVCDP_ 2. DA Philippine Coconut Authority (PCA) Kaanib Program 3. DAR Support Services Program 4. DENR - Forest Management Bureau (FMB) - National Greening Program (NGP), Community-Based Forest Management (CBFM), and other related programs/projects Coordination mechanism in the following eight (8) areas: 1. agricultural production; 2. training and technical assistance; 3. research and development; 4. marketing assistance; 5. machinery, equipment, facilities, and infrastructure; 6. rural credit and insurance; 7. policy and program formulation, monitoring, and evaluation and regulatory support; and 8. registry system of farmer benificiaries | This order aims to institutionalize the convergence initiative and coordination mechanism of DA-DAR-DENR-DILG NCI-SRD agencies for rubber, fiber crops, coffee, cacao, and other high value crops. | https://www.da.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/jmo01_s2020.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6429 | 2020 | 18th | An Act Establishing Cacao Research Development Center in the Municipality of Prosperidad, Province of Agusan Del Sur and Appropriating Funds Thereof | There shall be established, under the supervision of the Department of Agriculture-Bureau of Agricultural Research, Department of Science and Technology a cacao research and development center in the municipality of Prosperidad , province of Agusan del Sur. The Secretary of Agriculture shall include and the department's program the establishment of the Cacao Research and Development Center, the funding of which should be included in the annual general appropriations act. The local government of Prosperidad set aside funds from any available local revenue in an amount appropriate for the operationalization of the center . | A Cacao Research and Development Center is envisioned by the province of Agusan del Sur in order to support the thriving cacao communities and transform and empower them for sustainable cocoa farming and livelihood. | https://www.congress.gov.ph/legisdocs/basic_18/HB06429.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 7460 | 2020 | 18th | An Act To Declare The City Of Davao As The Chocolate And Cacao Production Capital Of The Philippines And For Other Purposes | The City of Davao is hereby declared as the cacao and chocolate production capital of the Philippines. The Department of Agriculture and the Department of Trade and Industry shall provide sustained programs for the grant of financial, technical, training, marketing, and other necessary assistance to ccao farmers an dentrepreneurs engaged in the production of chocolate products in Davao City and its contiguous localities. | The bill seeks to recognize the achievements of Davao City in attaining high volume of quality cacao production and in producing high quality chocolate products that gained for the country international recognition, as well as opened a frontier for higher trade and economic productivity in the country that can generate more employment, provide higher incomes and improve the quality of life of our people especially in the countryside. | https://www.congress.gov.ph/legisdocs/basic_18/HB07460.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 5585 | 2019 | 18th | An Act Creating A Cacao Research And Development Center, Authorizing The Appropriation Of Funds Therefor, And For Other Purposes | The Cacao Research and Development Center shall have the following general powers and functions in line with the research and development programs of the Department of Agriculture- Bureau of Agricultural Research (DA-BAR), Department of Science and Technology, Department of Trade and Industry (DTI), and National Economic Development Authority (NEDA): a. Educate and train all stakeholders of the cacao industry; b. Conduct relevant research, scientific study, and feasible marketing strategies c. Extend technologies d. Establish linkages with international organizations and other cacao development centers in other countries. | The bill seeks to address this issue by establishing a research and development center made specifically for cacao production to be able to compete globally and possible produce one of the best chocolates around the world. | https://www.congress.gov.ph/legisdocs/basic_18/HB05585.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Order | Senate Bill No. 320 | 2016 | 17th | An Act Establishing A National Program For The Cacao Industry Providing Funds Therefor And For Other Purposes, "Cacao Industry Development Act of 2016" | The National Cacao Development Council shall have the following general powers and functions: 1. Formulate the cacao development plan; 2. Educate and train all stakeholders of the cacao industry; 3. Conduct relevant research, scientific study and feasible marketing strategies; 4. Establish and develop effective production systems for cacao varieties; 5. Establisha and maintain productive, high yielding and good quality cacao varieties; 6. Establish and maintain germplasm collection and gene bank for cacao; 7. Update cacao processing technologies; 8. Develop effective and efficient marketing systems for cacaol 9. Establish linkages with national and international organizations and development centers of the cacao industry; 10. Coordinate with other government and non-government agencies involved in the development of the cacao industry. | The bill seeks to revive the dwindling cacao industry of the country and participate in the international markets for added income to our farmers. | http://legacy.senate.gov.ph/lisdata/2375820419!.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Resolution | House Resolution No. 1520 Senate Resolution No. 920 | 2014 | 16th | Resolution Directing The Committee On Agriculture And Food To Inquire, In Aid Of Legislation, Into The Status Of The Cacao And Chocolate Industry Of The Country And Maximize Its Full Potentials With The End In View Of Recommending Measures To Boost Local Production And Provide Livelihood Opportunities In The Rural Areas In Light Of A Projected World Deficit In Cacao Supply | It is hereby resolved by the House of Representatives, to direct the Committee on Agriculture and Food to inquire, in of legislation, into the status of the cacao chocolate industry of the country and maximize its full potential to the end in view of recommending measures to boost local production and provide livelihood opportunities in the rural areas in light of a projected world deficit in cacao supply . | The resolutions aims to help local farmers boost cacao production and revitalize the caco industry by looking into the situation of cacao and chocolate industry in the country. | https://www.congress.gov.ph/legisdocs/basic_16/HR01520.pdf http://legacy.senate.gov.ph/lisdata/1986116985!.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Guidelines/Strategies | Philippine National Standard for Cacao or Cocoa Beans PNS/BAFPS 58:2008 ICS 67.140.30 | 2008 | null | Philippine National Standard for Cacao or Cocoa Beans | Quality requirements: - shall be taken form ripe pods; adequately fermented and dried; free from smoky smell and other objectionable odor - shall be reasonably uniform in size - shall be reasonably free from broken beans, fragments and pieces of shell - shall be virtually free from foreign matter - shall be reasonably free from insect pests - moisture content of cacao beans in trade outside the producing country as determined at the first port of destination or subsequent points of delivery shall not exceed 7.5 % - consignment of bean shall contain not more than 2.5 % waste by weight | The PNS for cacao or cocoa beans sets a system of grading or classifying the cacao or cocoa beans derived from the harvested pods of cacao trees, Theobroma cacao L. Generally, cacao beans must be fermented and dried properly before marketing for various commercial uses and processing for various products. | http://spsissuances.da.gov.ph/attachments/article/828/PNS-BAFPS%2058-2008-Cacao%20Beans.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Law | Republic Act No. 7900 | 1995 | 9th | An Act To Promote The Production, Processing, Marketing, And Distribution Of High-Value Crops, Providing Funds Therefor, And For Other Purposes, "High-Value Crops Development Act of 1995" | It is hereby declared the policy of the State to accelerate the growth and development of agriculture in general, enhance productivity and incomes of farmers and the rural population, improve investment climate, competencies and efficiency of agribusiness and develop high-value crops as export crops that will significantly augment the foreign exchange earnings of the country, through an all-out promotion of the production, processing, marketing, and distribution of high-value crops in suitable areas of the country. HVCs are defined as crops other than traditional crops which include, but are not limited to: coffee and cacao, fruit crops (citrus, cashew, guyabano, papaya, mango, pineapple, strawberry, jackfruit, rambutan, durian, mangosteen, guava, lanzones, and watermelon), root crops (potato and ubi), vegetable crops (asparagus, broccoli, cabbage, celery, carrots, cauliflower, radish, tomato, bell pepper, and patola), legumes, pole sitao (snap beans and garden pea), spices and condiments (black pepper, garlic, ginger, and onion), and cutflower and ornamental foliage plants (chrysanthemum, gladiolus, anthuriums, orchids, and statice). | The Act aims to promote the production, processing, marketing, and distribution of high-value crops in suitable areas of the country. | https://www.congress.gov.ph/legisdocs/ra_09/Ra07900.pdf | Cacao | null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Cacao_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx |
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
ISP for Cacao
PCAARRD ISP on Cacao envisions to increase cacao bean yield, thereby increasing income of smallholder cacao farmers in the countryside.
Strategic R&D
Strategic R&D is DOST-PCAARRD’s banner program comprising all R&D activities that are intended to generate outputs geared towards maximum economic and social benefits
- Published On: July 4, 2024
Representative accessions screened for Lasiodiplodia theobromae or vascular streak dieback (VSD) using C4021t2 Molecular markers were generated from the completed DOST-PCAARRD funded project to identify...
- Published On: July 4, 2024
Laboratory mass rearing set-up of the lynx spider, Oxyopes javanus Cacao is a priority high value crop in the Philippines and one of the flagship...
- Published On: July 4, 2024
Photographs showing treated cacao pod with cacao mirid bugs (CMB) introduced into plastic cups (left) and treated pods in a cacao tree (right). Field assessment...
Technologies
Products, equipment, and protocols or process innovations developed to improve productivity, efficiency, quality, and profitability in the agriculture and aquatic industries, and to achieve sustainable utilization and management of natural resources
- Published On: November 26, 2021
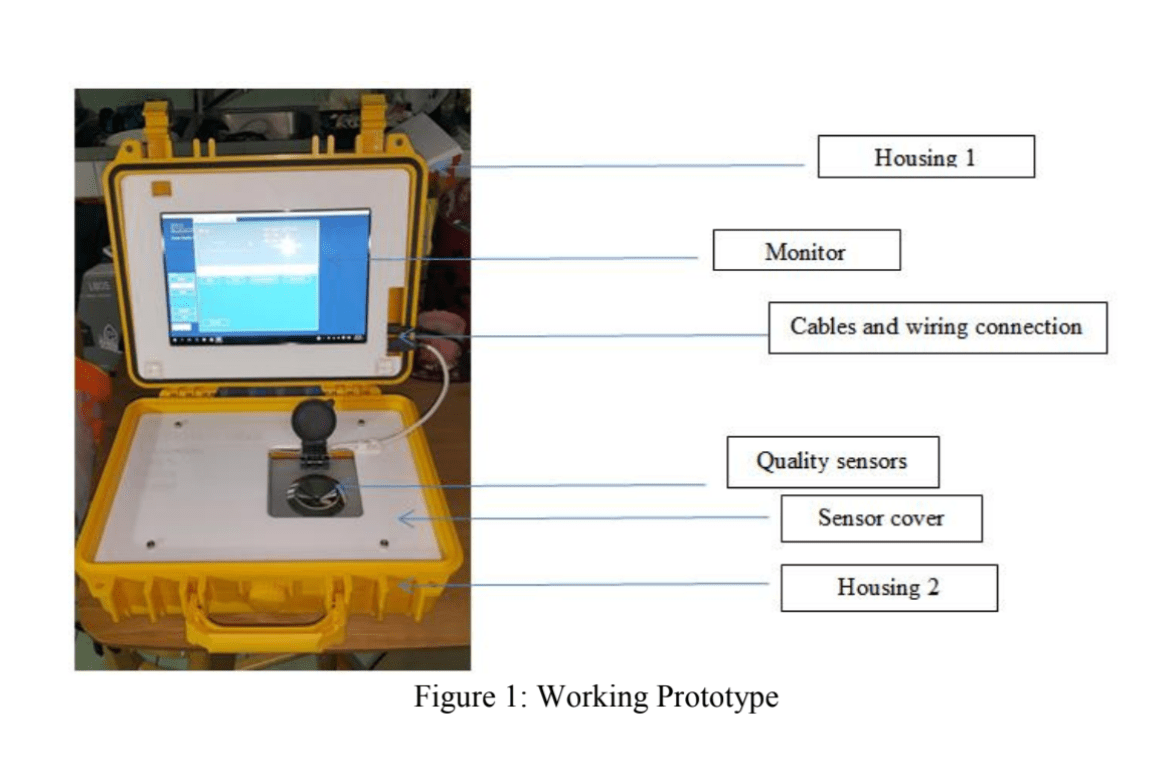
A device was developed that can measure the quality of wet cacao beans prior to fermentation and good quality beans. The instrument comprises several sensors...
Technology Transfer Initiatives
Technology Transfer initatives ensure that the outputs of R&D and innovations are transformed into viable and applicable technologies that help intended users.
- Published On: July 4, 2024
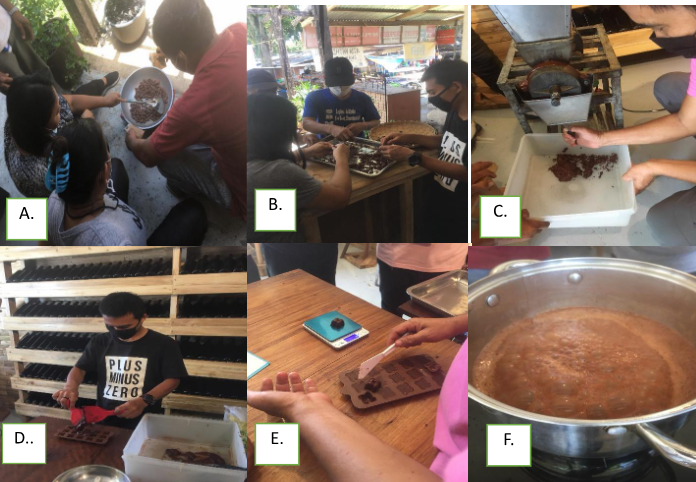
The project team and the participants during the actual demonstration of the following: (a) roasting, (b) sorting, (c) grinding, (d) molding, (e) de molding, and...
- Published On: November 26, 2021
The project will focus on the 12 municipalities in the 1st District of Zamboanga del Sur. With the assistance of Cong. Yu and other agencies,...
- Published On: November 26, 2021
This project is a technology transfer initiative to showcase the technology convergence of the latest S&T practices for cacao rehabilitation in Davao Oriental. It also...
Capacity Building
Capacity building efforts of DOST-PCAARRD seek to develop and enhance the R&D capabilities of researchers and academic or research institutions through graduate assistantships, non-degree trainings & development, and/or upgrading of research facilities.
Manpower Development
Policy Research & Advocacy
Analysis of policy concerns and advocacy of science-informed policies ensures that the AANR policy environment is conducive for S&T development and investments.

Competitiveness of Philippine Cacao Production under the ASEAN Economic Community
Producing cacao in the country was found to be cheaper relative to importing from other countries, which makes Philippine cacao competitive under the import substitution scenario. This implies that the country should focus on improving the local industry. Sadly, results show that the country will lose its import competitiveness if yield (1.50 mt/ha) declines by only 9 percent. However, it also highlighted that the country is close to becoming export competitive if given a 2 percent increase in yield or a 2 percent decrease in domestic cost.
Reference(s):
Lapiña, G. F. and Andal, E. T. (2017). ASEAN Economic Community: Opportunities and Challenges for the Crops Sector. Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: Philippine Council for Agriculture, Aquatic and Natural Resources