Abaca
Industry Strategic Science and Technology Program
Abaca Industry Profile
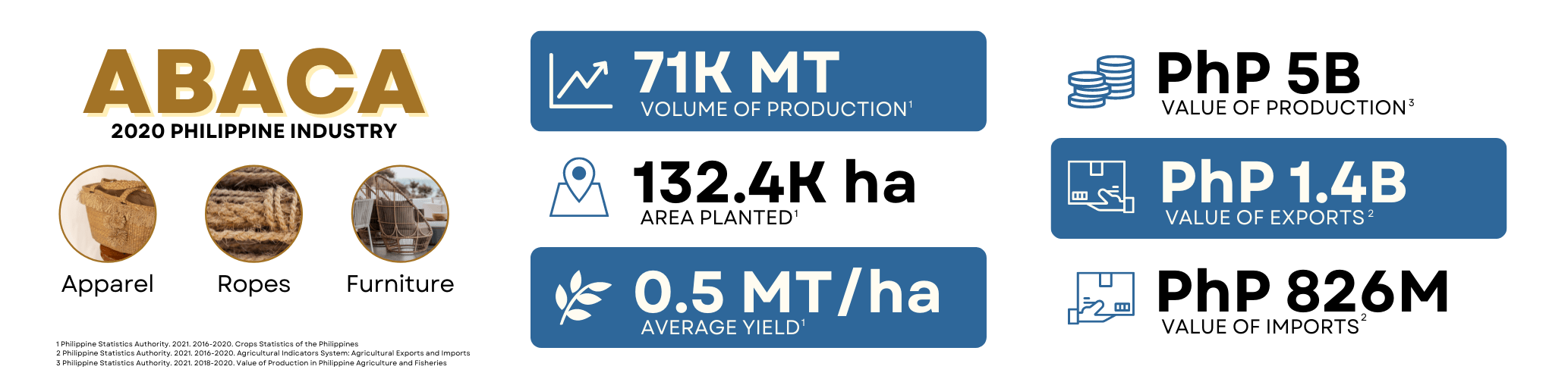
Abaca, also known as Manila Hemp with the scientific name Musa textilis, is a natural leaf fiber species of banana grown as a commercial crop native in the country. Its leaf stems are harvested for its natural fiber that possesses valuable properties such as buoyancy, high porosity, high tensile and folding strength, and resistance to saltwater damage. According to Philippine Fiber Industry Development Authority (PhilFIDA), the Philippines, as the world’s top exporter of abaca, supplies 85 percent of the global abaca fiber production and earns US$80 million per year. Based on the data from the Philippine Statistics Authority (PSA), as of 2019, Bicol Region remained the top abaca producer with 28.94 thousand metric tons or 40.1 percent contribution to the total abaca production, followed by Eastern Visayas and Davao Region with 17.5 percent and 12.5 percent shares, respectively. Bicol Region also had the largest area planted for abaca, with 43.16 thousand hectares in 2019. With its durability, flexibility, and resistance to saltwater damage, it is commonly used in fishing lines and nets, ropes, and twines. Other applications of abaca involve its use as a material in manufacturing bags, carpets, diapers, pill coatings, textile, and surgical masks.
Problems in the Industry
One of the most significant problems that the abaca industry faces is natural calamities. These calamities, such as typhoons, cause an increase in the production cost, thereby increasing the final products’ price. The prevalence of pests and diseases is also a common concern in the industry resulting in low fiber yield and poor fiber quality.
Other constraints include the following:
- Limited supply of quality abaca planting materials;
- Lack of high yielding and virus-resistant planting materials;
- Poor technology adoption of farmers;
- General lack of facilities for transport and drying;
- Insufficient support in product marketing and promotion; and
- Lack of financial capability of abaca farmers.
Abaca Policies
| Policy Type | Policy Number | Policy Year | Congress | Policy Title | Policy Description | Policy Objective | Policy Link | Commodity | Classification | info_encoder_stamp | info_date_stamp | info_quashing_remarks | filepath |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Law | Republic Act No. 11700 | 2022 | 18th | An Act Declaring The Province Of Catanduanes As The Abaca Capital Of The Philippines | In recognition of its status as the country's biggest producer of abaca and making the Philippines world-renowned as "Manila Hemp" in the fiber industry, and in support to agricultural development of the province, it is hereby declared that Catanduanes be the Abaca Capital of the Philippines. | The law aims to recognize the importance of abaca industry and its development as a driver of rural development not only because of its singular potential as a raw material that can increase the country's export earnings tremendously, and put the name of the country in the map of the world for producing the biggest volume of abaca fiber, but for having provided livelihood to many small farmers in the countryside. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2022/04/15/republic-act-no-11700/ | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Guidelines/Strategies | Philippine National Standard for Abaca Fiber- Grading and Classification - Decorticated, PNS/BAFS 181:2016 | 2016 | null | Philippine National Standard for Abaca Fiber- Grading and Classification - Decorticated, PNS/BAFS 181:2016 | This Standard specifies requirements and establishes a system of grading and classifying of commercial grades of decorticated abaca fiber. In all normal grades subject to the special provisions for each grade under Section 5 and the tolerances allowed, decorticated abaca fiber shall meet the following requirements: - The tensile strength of the decorticated abaca fiber ranges from 19.5 to 32.6 kilogram force per gram meter (kgf/g.m). - The minimum length shall not be less than 60 centimeters. - The abaca fiber must be of uniform color according to the grade. - The abaca fiber must be of the same kind of decorticating. - The abaca fiber must not be soiled, stained or discolored and must be free from foreign matters. | This standard intends to provide specification on the requirements and grading quality of decorticated abaca fiber for local consumption and international trade. | http://www.philfida.da.gov.ph/images/Publications/PNS/PNSBAFS1812016AbacaFiberDecorticated.pdf | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Guidelines/Strategies | Philippine National Standard for Abaca Fiber- Grading and Classification - Hand stripped and Spindle / Machine stripped, PNS/BAFS 180:2016 | 2016 | null | Philippine National Standard for Abaca Fiber- Grading and Classification - Hand stripped and Spindle / Machine stripped, PNS/BAFS 180:2016 | This Standard specifies requirements and establishes a system of grading and classifying of commercial grades hand-stripped and spindle/machine -stripped abaca fiber. In all normal grades subject to the special provisions for each grade and the tolerances allowed, hand-stripped and spindle/machine-stripped abaca fiber shall meet the following requirements: - The tensile strength of abaca fiber ranges from 35 to 55 kilogram force per gram meter (kgf/g.m). - The minimum length shall not be less than 60 centimeters - The abaca fiber must be of uniform color according to the grade. - The abaca fiber must be of the same kind of stripping. - The stripped abaca fiber must not be soiled, stained or discolored and must be free from foreign matters | This standard intends to provide specification on the requirements and grading quality of hand stripped and spindle/machine stripped abaca fiber for local consumption and international trade. | http://www.philfida.da.gov.ph/images/Publications/PNS/PNSBAFS1802016AbacaFiberHandstrippedandMachineStripped.pdf | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Order | Executive Order No. 538 | 2006 | null | An Order Repealing Executive Order No. 502 “Banning the Harvesting, Gathering, Buying, Selling and Mutilating of Matured And Young Leafsheaths Of Abaca Plants (Musa Textiles Nee) for Commercial Purposes” | The harvesting, gathering, buying, selling and mutilating of mature and young leafsheaths (locally known as “bakbak” or “umbak”) of abaca plant was prohibited by Executive Order No. 502, for the primary purpose of preventing the spread of abaca diseases which has affected certain areas in Southern Leyte and adjoining areas. The ban, however, resulted in a disruption in the material supply chain of furniture, furnishing and handicrafts exports that use “bakbak” or “umbak” as raw materials, thus resulting in significant economic losses to stakeholders. The Local Government units of disease-infected barangays in Southern Leyte and Leyte provinces are hereby encouraged to strictly implement their ordinances restricting the transport of “bakbak” or “umbak” until the abaca disease is sufficiently controlled. | The order seeks to repeal EO No. 502 s. 2006. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2006/07/04/executive-order-no-538-s-2006/ | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Order | Executive Order No. 502 | 2006 | null | An Order Banning the Harvesting, Gathering, Buying, Selling and Mutilating of Matured And Young Leafsheaths Of Abaca Plants (Musa Textiles Nee) for Commercial Purposes” | The abaca plant, which is indigenous to the Philippines, is producing the natural fiber known worldwide as Manila Hemp. It is considered one of the high value commercial crops contributing an average of P4.5B revenue for the country and providing direct and indirect employment to an estimated 1.5 million Filipinos. There is an unabated harvesting, gathering, buying, selling, and mutilating of its matured and young leafsheaths known locally as “bakbak” or “umbak”, thus slowly decimating its existence and threatening the source of fiber. These activities will and in numerous cases have aggravated further the spread of abaca viral diseases particularly the abaca bunchy-top, abaca mosaic and the abaca bract, and other microorganisms mostly by mechanical means and the transporting of these abaca “umbak” or “bakbak”. | The order seeks to ban the harvesting, gathering, buying, selling, and mutilating for commercial purposes of its matured abaca plants and its young leafsheaths known locally as “bakbak” or “umbak” or any terms that may be commonly used. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2006/02/02/executive-order-no-502-s-2006/ | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Law | Republic Act No. 9242 | 2004 | 12th | An Act Prescribing the Use of the Philippine Tropical Fabrics for Uniforms of Public Officials and Employees and for Other Purposes | The use of Philippine tropical fabrics is prescribed for official uniforms of government officials and employees and for the purposes which require the use of fabrics in government offices and functions. Philippine tropical fabrics used for the uniforms of government officials and employees, and for other government purposes shall be purchased from local sources in accordance with law. For the initial implementation of this Act, an amount of P60 Million from the Agricultural and Fisheries Modernization Act Fund was allotted to the Fiber Industry Development Authority (FIDA) of the Department of Agriculture (DA) for the promotion of the commercial production of plant fibers and for the conduct of continuing research on the improvement of the process of extracting plant fibers. | The law aims to instill patriotism and nationalism among the people, especially public officials and employees, who shall at all times be loyal to the Republic and the Filipino people, by requiring the use of Philippine tropical fabrics for official uniforms of government officials and employees. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2004/02/10/republic-act-no-9242/ | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Proclamation | Proclamation No. 222 | 2002 | null | Declaring The Last Week of July of Every Year as National Abaca Week | Abaca is indigenous to the Philippines and is one fiber that has made the Philippines known all over the world. It is a traditional export commodity generating much needed foreign exchange revenues and is one of the major sources of employment especially in the countryside. The Philippines is the world’s biggest producer of abaca fiber supplying 85% of the global requirement. Abaca is acknowledged the world over as the best material for cordage and various specialty paper products such as paper currency; | The observance of a National Abaca Week will help promote, enhance and instill nationwide awareness and appreciation of the importance and value of this truly Filipino fiber to the Philippines and the national economy. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2002/07/16/proclamation-no-222-s-2002/ | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Order | Executive Order No. 709, s. 1981 | 1981 | null | Creating a Ministry of Trade and Industry | Under Section 8 of EO No. 709, the Fiber Industry Development Authority (FIDA) was established to absorb the functions of the abolished Bureau of Fiber and Inspection Service and of the Abaca Industry Development Authority. The new Authority falls under the administrative supervision of the then Minister of Agriculture, who shall undertake the integration of the functions, applicable appropriations, records, equipment, property, and such personnel as may be necessary, of the two abolished entities. | The order creates the Fiber Industry Development Authority (FIDA) . | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/1981/07/27/executive-order-no-709-s-1981/ | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Law | Presidential Decree No. 1208 | 1977 | null | Creating The Abaca Industry Development Authority | The Abaca Industry Development Authority, referred to as the AIDA, was established and attached to the Department of Agriculture for the purpose of promoting the accelerated growth and development of the abaca industry in all its aspects. AIDA shall rationalize the research, production, processing, and marketing of abaca, and provide continued leadership and support for the integrated development of the industry. | The law seeks to create an agency that will regulate abaca production, processing, distribution, sale, transport and storage. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/1977/10/08/presidential-decree-no-1208-s-1977/ | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Law | Republic Act No. 4967 | 1967 | 6th | An Act Extending the Life of the Abaca and Other Fibers Development Board, Maintaining its Own Funds Therefor and for Other Purposes | The Program shall cover the following phases: 1. Production and distribution of planting materials to be disposed of at nominal costs, for the rehabilitation of depleted plantations and expansion to newly-opened areas; 2. Improvement and operation of fiber extraction methods to reduce the cost of production and improve the quality of the fibers; 3. Development, establishment and promotion of new industries using abaca and other fibers as raw materials; 4. Abaca and other fibers scientific, agricultural, industrial and commercial research; 5. Abaca and other fibers local and foreign trade promotion; and 6. General administration. | The law aims to rehabilitate and expand the abaca and other fibers industry of the country to maintain its world supremacy and the world demand for abaca and other Philippine fibers and their by-products, and to provide adequate measures to ensure permanent stability in the production and consumption of abaca and other fibers. | https://lawphil.net/statutes/repacts/ra1967/ra_4967_1967.html | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx | |
| Order | Executive Order No. 42, s. 1954 | 1954 | null | Creating a Committee to Study the Problems of Abaca Industry | The Committee is authorized to call upon any department, bureau, office, agency or instrumentality of the Government for such assistance or information as it may require in the performance of its functions, and for this purpose, it shall have access to, and the right to examine, any books, documents, papers or records thereof. | The order aims to create a committee to study the problems of the abaca industry, with particular reference to the high cost of production and the loss of markets. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/1954/07/06/administrative-order-no-42-s-1954/ | Abaca | null | Jeff U. | 05/27/2025 | C:\Users\MISD-Jeff\Documents\PCAARRD\Formatting\Output\Abaca_2025-05-27_processed.xlsx |
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority. 1990-2023.
ISP for Cacao
The ISP for abaca aims to improve and aid in sustaining the country’s stand as the world’s leading producer of abaca through varietal improvement, pest and disease management, and product development and value addition to increase farm productivity, thereby increasing the farmers’ income.
Strategic R&D
Strategic R&D is DOST-PCAARRD’s banner program comprising all R&D activities that are intended to generate outputs geared towards maximum economic and social benefits
- Published On: October 23, 2023
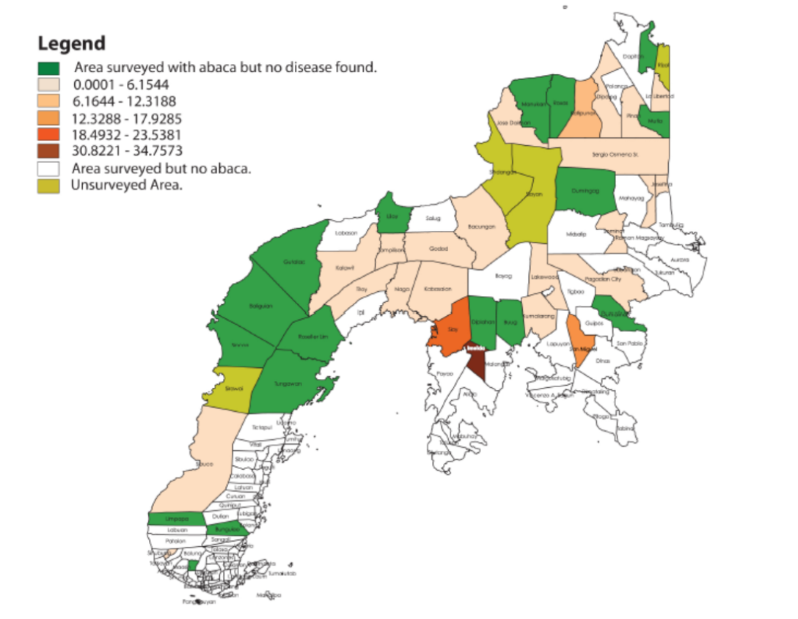
The project titled “Mapping the Distribution of Abaca Bunchy Top in Different Cropping Systems and Analyzing Epidemic Risks in the Zamboanga Peninsula” coordinated with local...
- Published On: October 23, 2023
The project titled “Revitalizing the Abaca Industry through S&T Interventions for Higher Crop Productivity Using High-Yielding and Bunchy Top- Resistant Abaca Hybrids” was implemented to...
- Published On: October 23, 2023
To meet the potential demand of abaca fibers for the pulp and paper industry, DOST-PCAARRD funded a project titled “Advanced Evaluation of Abaca Hybrids with...
Technologies
Products, equipment, and protocols or process innovations developed to improve productivity, efficiency, quality, and profitability in the agriculture and aquatic industries, and to achieve sustainable utilization and management of natural resources
- Published On: October 23, 2023
With the abaca stripping machine, four persons can harvest one hectare of abaca plantation in 7-8 days. It weighs only 93 kg and can be...
Technology Transfer Initiatives
Technology Transfer initatives ensure that the outputs of R&D and innovations are transformed into viable and applicable technologies that help intended users.
- Published On: October 23, 2023
The project aimed to elevate the socio-economic status of abaca farmers in the Community Empowerment thru S&T (CEST) communities in Sogod, Southern Leyte by making...
Capacity Building
Capacity building efforts of DOST-PCAARRD seek to develop and enhance the R&D capabilities of researchers and academic or research institutions through graduate assistantships, non-degree trainings & development, and/or upgrading of research facilities.
Infrastructure Development
Manpower Development
Policy Research & Advocacy
Analysis of policy concerns and advocacy of science-informed policies ensures that the AANR policy environment is conducive for S&T development and investments.

Competitiveness of Philippine Abaca Industry under the ASEAN Economic Community
Abaca production in the Philippines was competitive under export trade and import substitution scenarios. Exporting abaca is an excellent opportunity for the country to earn foreign exchange since the Philippines can compete globally. To sustain the country’s competitiveness in abaca, yield (22.56 mt/ha) must not decline by 82 percent, or domestic cost must not increase by 104 percent.
Reference(s):
Lapiña, G. F. and Andal, E. T. (2017). ASEAN Economic Community: Opportunities and Challenges for the Crops Sector. Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: Philippine Council for Agriculture, Aquatic and Natural Resources