In this Article
Digitalization in agri-food systems offers ways to improve processes, increase productivity, meet the demands of consumers through the market, reduce emissions, and help meet climate change targets.

Source: ADB
A rise in digital applications caused by the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrates how technology can modernize agriculture and change food systems. When lockdown and quarantine hindered traditional logistics, investing in digital technology to strengthen ties with the market suddenly became the logical and only method to connect producers and consumers.
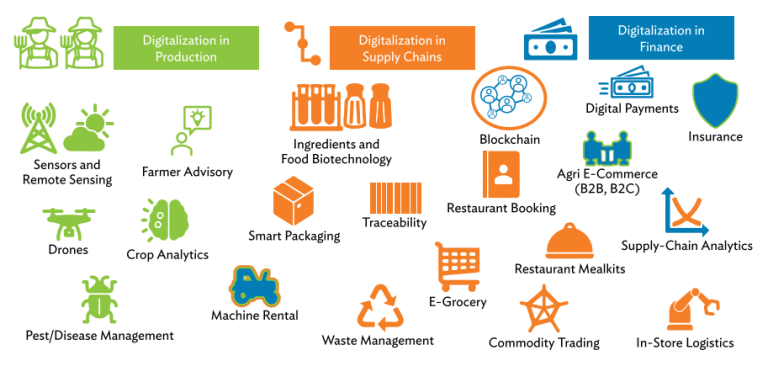
Digital technology can impact decision points in the agri-food system, including (1) biotechnology for crop and animal improvement, (2) novel environments for farming, (3) product integrity and fraud prevention, (4) supply chain logistics, infrastructure, and risk management,(5) novel food, and (6) waste reduction and waste valorization.
There are two significant impacts of digital technology in domains where policymakers and practitioners have long acknowledged the need for transformation. These include providing low-cost, timely advisory inputs and connecting producers with final markets and consumers. Digitally based approaches are ideally suited for these functions. One of the essential tools for progressive transformation is using mobile phones for both subsets of agri-food decision-making. The introduction of Ama Krushi, a mobile-based customized advisory service for farmers in Odisha, India, is one example of the first of these significant development areas.
Reference:
Asian Development Bank. (December 2022). Battling Climate Change and Transforming Agri-food Systems. Retrieved November 21, 2023 from




