In this Article
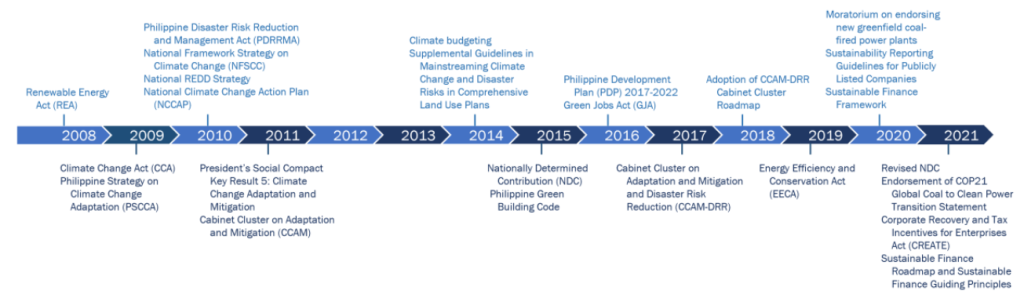
With the effects of climate change, the Philippines created a climate change agenda across sectors and government institutions and put important national policies and legislation into place.

Source: World Bank
The establishment of a risk-based framework for national and sub-national climate policies was set in the National Framework Strategy on Climate Change 2010-2022 (NFSCC) to strengthen community adaptation capacity and boost ecosystem resilience to climate change, and maximize mitigation opportunities in the direction of sustainable development. The plan viewed mitigation as a chance to take use of the nation’s greenhouse gas mitigation potential, utilizing regulations like the Renewable Energy Act (REA) while delivering development co-benefits such as pollution reduction.
As of now, there are 22 agencies required to execute the climate agenda, but they only have limited capacity to do so due to lack of rules and regulations. However, individual line departments, including the Department of Energy (DOE), Department of Transportation (DOTr), Department of Agriculture (DA), Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR), and Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH) are responsible for implementing the adaptation and mitigation measures. Thus, local governments are being given more responsibility for addressing climate change. LGUs are key players in enhancing a community’s resilience to natural disasters and climate change. They are in charge of local governance in 81 provinces, 146 cities, 1,488 municipalities, and 42,046 barangays in the country as of September 2020.
Other government programs that support climate actions include the development of frameworks to green the financial sector and instruments at the regulatory level, adaptation of private sector energy companies to maintain customer service while safeguarding future revenues, minimizing costs and reducing losses, implementation of various adaptive social protection (ASP) programs to help people adapt to climate change, and integration of adaptation concepts into health, science, social studies and values education from kindergarten to senior high school.
Reference:
World Bank Group. (2022). Country Climate and Development Report: Philippines. Retrieved June 21, 2023, from https://reliefweb.int/report/philippines/philippines-country-climate-and-development-report-2022