In this Article
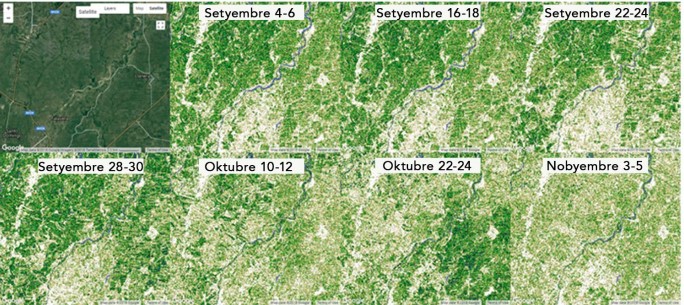
A web-based system that uses GIS, remote sensing and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index or the index of plant “greenness” or photosynthetic activity to monitor the status of agricultural crops. This can be used to determine the following: crop damage assessment (typhoon, drought, and pests), land use/cover change, vulnerability assessment, identify possible breeding ground of major insect pests, weather conditions in areas without weather station.








