Rubber
Industry Strategic Science and Technology Program
Rubber Industry Profile
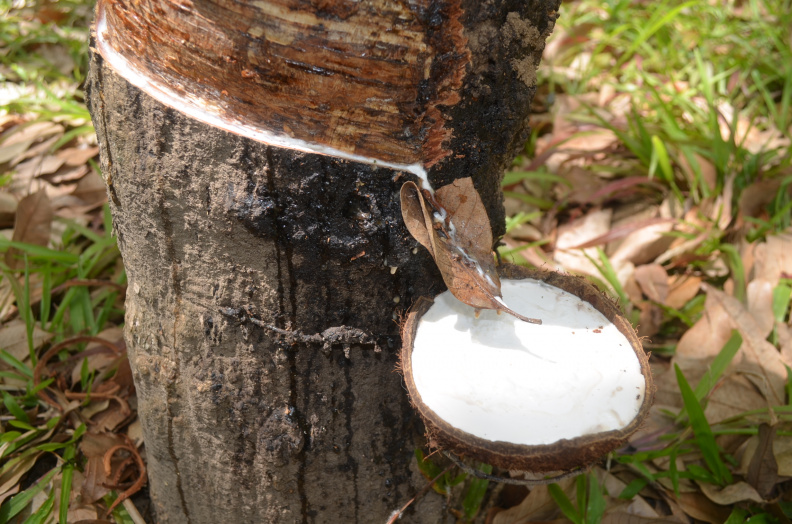
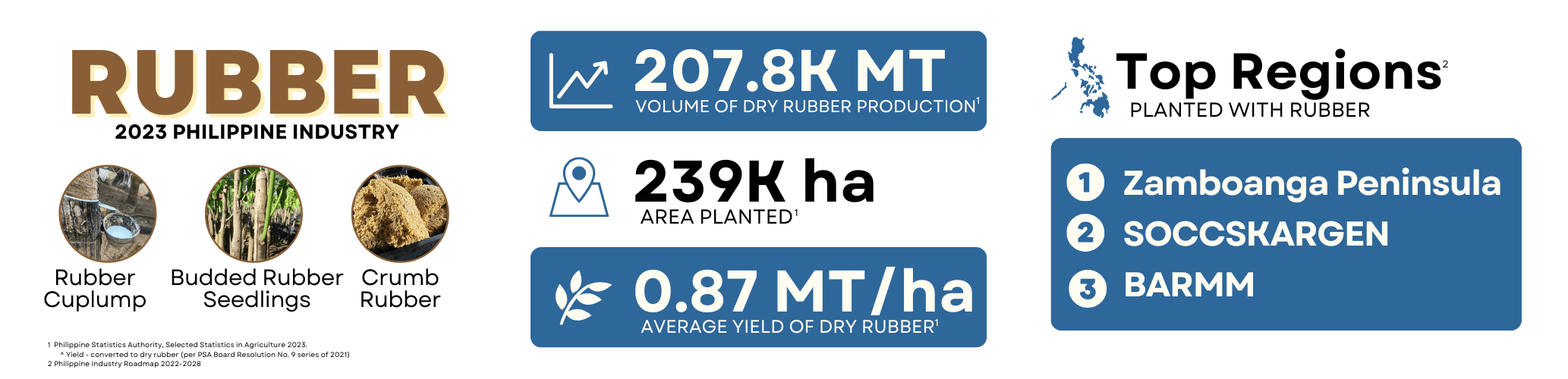
Rubber is one of the most popular agro-industrial crops in Southeast and South Asia. Major countries producing rubber worldwide include Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, China and India. Scientifically known as Hevea brasiliensis, the rubber tree is a robust perennial crop with natural rubber (NR) as its main product. Majority of rubber production in the Philippines is sourced from Mindanao, wherein the country ranked 10th in the world in terms of natural rubber production back in 2014. As of 2023, the top rubber-producing province in the country is Cotabato with 110,764 metric tons (MT) of coagulated cup lump produced. This is followed by Zamboanga Sibugay and Basilan with 108,111 MT and 69,392 MT, respectively. On the other hand, the top producing regions are Zamboanga Peninsula, SOCCSKSARGEN and BARMM.
The three main sectors of the Philippine Rubber Industry are upstream, midstream, and downstream. The upstream sector includes input suppliers and rubber planters producing latex and cup lumps. The midstream sector involves processors of Technically Specified Rubber (crumb rubber and air-dried sheets), latex concentrate, as well as traders and exporters. The downstream sector comprises manufacturers of tires, automotive parts, sports products, and footwears. Upstream and midstream activities are primarily located in Mindanao, while downstream activities are in Luzon and Visayas.
Problems in the Industry
Like any other commodities, rubber is also faced with several problems such as
- Low farm productivity
- Reduced latex quality,
- Inadequate Quality Planting Material (QPM) supply
- Poor site development, and
- Low technology adoption.
Low farm productivity is attributed to the extensive use of low-yielding seedlings, mislabeled clones as high-yielding, poor tapping practice, non-adoption of fertilization schedule and also, climate change. The reduced latex quality also results to the lower price of raw natural rubber. This can be caused by poor tapping coagulation practice (e.g. use of sulphuric acid), reduced rubber tree life and insufficiency of trained farmers/tappers. Although there has been an increasing trend in areas planted to rubber, there is still a problem with the availability and supply of QPM and poor nursery and budwood management practices. Among the hindrance to rubber expansion is poor site development which can be attributed to insufficient planning and site matching tools, limited studies on suitable rubber planting sites and impacts of climate change.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Rubber Policies
| Policy Type | Policy Number | Policy Year | Congress | Policy Title | Policy Description | Policy Objective | Policy Link | Commodity | Classification | info_encoder_stamp | info_date_stamp | info_quashing_remarks | filepath |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bill | Senate Bill No. 606 | 2022 | 19th | An Act To Develop The Rubber Industry, Establishing For The Purpose The Philippine Rubber Industry Development Board, Defining Its Powers And Functions, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | The Philippines was known to be among the top producers of rubber until the 1980s when the demand for tires and other rubber products slackened due to the decline in the economies of Japan and Europe. In the recent years, the country displayed vitality with the rising demand for natural and synthetic rubber. Much of this demand would stem from the rise of industries making use of rubber such as the automotive, footwear, and healthcare industries. Rubber production in the country mainly thrives in Mindanao due to its agro-climate suitable in cultivating rubber, but some farmers are now planting the same in Luzon and Visayas for its lucrative value. With the increasing global and domestic demand for natural rubber, now is an opportune time to strengthen the rubber industry of the country. | This bill provides a means of producing a steady supply of quality rubber by enhancing the competitiveness of the processing and manufacturing of rubber and rubber-based products. It also aims to establish the Philippine Rubber Industry Development Board (PHILRUBBER), which will further strengthen the foundations of the Philippine rubber industry to its full potential by creating more opportunities in the agricultural and manufacturing sector. | https://legacy.senate.gov.ph/lisdata/3839434848!.pdf | Rubber | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Rubber_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 2331 | 2022 | 19th | An Act To Develop The Rubber Industry, Establishing For The Purpose The Philippine Rubber Industry Development Board, Defining Its Powers And Functions, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | It is the policy of the State to establish a strong foundation for more inclusive growth where it is shall be easier for the marginalized economic sectors to participate in economic progress through job creation and encouragement of entrepreneurship. The government, in partnership with the private sector, shall improve the productivity of agriculture and enhance the global competitiveness of the industry and services sectors. Toward this end, the government, with the active support of the private sector, shall endeavor to achieve a balanced, integrated, and sustainable development of the country's rubber industry, the Philippines being frequently among the top 10 exporters of raw or semi-processed rubber, and being favorably situated in Southeast Asia which accounts for 90% of the world's output of natural rubber. The government shall undertake to develop Philippine rubber as a major participant in the rubber global value chain by accelerating the industry's overall growth through the following: (a) Expanding and improving the productivity and quality of natural rubber production for domestic and global markets; (b) Enhancing the competitiveness of the processing and manufacturing of rubber and rubber-based products, setting international quality control standards and ensuring adherence thereat; (c) Encouraging diversification through product upgrading which involves the production of better quality and higher valued semi-processed rubber; and (4) Promoting public-private partnership to push forward the programs and projects that will optimize natural and manufactured rubber product utilization. | This bill seeks to establish the Philippine Rubber Industry Development Board. The Board will be tasked to oversee and coordinate the initiatives of government agencies, the private sector, the academe and other concerned groups to spur rubber industry growth and development. Specifically, the Board will evaluate the Philippine rubber industry performance, focusing on issues and concerns, prospects, threats and opportunities, and other constraints to growth, and identifying agencies that can best address the areas of concern from the production/cultivation stage, to processing/manufacturing, trading and market distribution of rubber and its allied products. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB02331.pdf | Rubber | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Rubber_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | Senate Bill No. 526 | 2019 | 18th | An Act To Develop The Rubber Industry, Establishing For The Purpose The Philippine Rubber Industry Development Board, Defining Its Powers And Functions, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | With the rising demand for natural and synthetic rubber, it is expected that demand for rubber will reach up to 15.238 million tons by the year 2022. Much of this demand would stem from the rise of industries making use of rubber such as the automotive, footwear, and healthcare industries. The rubber industry in the Philippines produced up to about 181,313 MT of rubber in the year 2016, which was fewer by 8.92% than in 2015. Furthermore, the overall export performance of rubber in the Philippines declined. The total export revenue generated by the rubber industry in 2016 was only US135.08 million, whereas in 2012, the total export revenue was US405.99 million. | This measure provides a means of producing a steady supply of quality rubber by enhancing the competitiveness of the processing and manufacturing of rubber and rubber-based products. It also aims to establish the Philippine Rubber Industry Development Board (PHILRUBBER), which will further strengthen the foundations of the Philippine rubber industry to its full potential by creating more opportunities in the agricultural and manufacturing sector. | https://legacy.senate.gov.ph/lisdata/3090927762!.pdf | Rubber | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Rubber_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 3280 | 2019 | 18th | An Act Creating The Philippine Rubber Industry And Technology Council Amending For The Purpose Republic Act No. 10089 Known As An Act Creating The Philippine Rubber Research Institute To Develop The Philippine Rubber Industry And For Other Purposes | It is a declared policy of the State to develop self-reliant industries effectively controlled by Filipinos, encourage investments and provide incentives to private enterprise, promote employment and livelihood opportunities for the poor, ensure well-balanced ecology in the use of natural resources for industrial purpose, and prioritize education and training particularly in science and technology for sustainable development. In support of these State policies, the establishment of the Philippine Rubber Industry and Research Technology aims to comprehensively realize the goals of human empowerment and economic development in the countryside through programs and projects that will increase rubber production and provide processing equipment to enhance quality rubber production for the benefit of small rubber farmers stakeholder (smallholder) producers and processors. | This bill aims to revisit and possibly amend some provisions of the RA 10089 by establishing and strengthening the rubber industry in the country making itself as a government institution by way of a Council involving various government agencies, one of which is the Department of Science and Technology (DOST) to support the needed Research Development in modern technology not only the rubber processing industry but in the modern production technique. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_18/HB03280.pdf | Rubber | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Rubber_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Republic Act | Republic Act No. 10089 | 2010 | 14th | An Act Creating The Philippine Rubber Research Institute To Develop The Philippine Rubber Industry And For Other Purposes | SEC. 2. Declaration of Policy.—It is a declared policy of the State to develop self-reliant industries effectively controlled by Filipinos, encourage investments and provide incentives to private enterprise, promote employment and livelihood opportunities for the poor, ensure well-balanced ecology in the use of natural resources for industrial purposes, and prioritize education and training particularly in science and technology for sustainable development. In support of these State policies, the establishment of the Philippine Rubber Research Institute aims to comprehensively realize the goals of human empowerment and economic development in the countryside through programs and projects that will increase rubber production in the country, and improve quality of life especially in poor rural communities that depend primarily on this industry. | This Act aims to establish the Philippine Rubber Research Institute to comprehensively realize the goals of human empowerment and economic development in the countryside through programs and projects that will increase rubber production in the country, and improve quality of life especially in poor rural communities that depend primarily on this industry. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2010/05/13/republic-act-no-10089/ | Rubber | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Rubber_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx |
Rubber Programs
| Agency | Program Title | Program Description |
|---|---|---|
| Philippine Rubber Research Institute (PRRI) | Capacity Development Program for Rubber Farmers' Associations and Cooperatives | Training on Capacity Development Program to the TIMARBEMCO members at Tungawan, Zamboanga Sibugay on June 24-25, 2020. |
| Philippine Rubber Research Institute (PRRI) | Capacity Development Program for Rubber Farmers' Associations and Cooperatives | A two-day training on Capacity Development Program for rubber Farmers’ Associations and Cooperatives was conducted at Brgy. Timalang, Ipil, Zamboanga Sibugay on June 22-23, 2020. The said activity participated with twenty-three rubber farmers from Timalang Rubber Farmers’ Association. |
| Philippine Rubber Research Institute (PRRI) | Philippine Rubber Research Institute Seeds Distribution | PRRI staff on its implementation of rubber-based intervention project entitled ‘Gulayan sa Gomahan’ has gone to the area for seeds distribution to the identified rubber farmers and tappers at Dalisay, Titay, Zamboanga Sibugay |
| Philippine Rubber Research Institute (PRRI) | Collection of Rubber promising and potential clones (Special Project) | Germplasm collection have provided original materials for plant breeding program and crop improvement. Because of their genetic diversity and possible occurrence of particular desirable genes, germplasm collection are useful targets to plant breeders. Recently, many of germplasm are being lost worldwide due to habitat destruction, invasion of foreign species, and reliance on fewer high yielding strains. Therefore, maintaining germplasm collection will be utilized based on its characters of immediate perceived value or its potential variation. Furthermore, it can also be used to better understand the properties and performance of the plants, particularly at the genomic level. Nowadays, counties all over the world have set up facilities for conservation, characterization and utilization of germplasm collections of various crops either directly or indirectly. |
| Philippine Rubber Research Institute (PRRI) | PRRI- IRRDB Multilateral Clone Exchange Trial (Special Project) | The Multilateral Clone Exchange Program has been organized by the International Rubber Research Development Board (IRRDB) to preserve potential clones of good performance. Thus, popular clones evolved in different countries are being introduce to member countries and evaluate under the local agro climatic conditions. Fifteen countries under IRRDB membership are participating. In total there are forty-nine clones to be exchanged by 12 countries. The Philippines contributed by giving its lone clone USM1 to all participating countries. While other countries such as; Cambodia, Cameroon and Guatemala are recipients only |
| Philippine Rubber Research Institute (PRRI) | Phenotypic Diversity of Small-Scale Hevea Germplasm Grown in PRRI Nursery at their Juvenile Stage | Proper identification of rubber clones plays a vital role in crop management system and research. Although clones do not exhibit highly distinct variations. Most of them possess differences in certain minor, but more or less stable morphological features which can be used for identification. Collection of germplasm resources is a significant component of any conservation program and is likely costly and logistically difficult. Germplasm collections in genebank repositories remain of less value unless characterized and evaluated for their range of variability and what they could offer for research and other uses. It is highly important to characterize and evaluate cultivar to look for novel gene sources that are potential and useful for future breeding study. This merited sufficient concern for the urgent conservation of its genetic resources which serves dual purposes; conservation per se and for the immediate and/or future utilization (Hodkin et al., 1995), as with other species. This study is being conducted to assess the genetic diversity of the collected hevea germplasm under PRRI nursery condition at juvenile stage to facilitate efficient selection of parent materials for hybridization and the identification of highly heterotic groups. |
ISP for Rubber
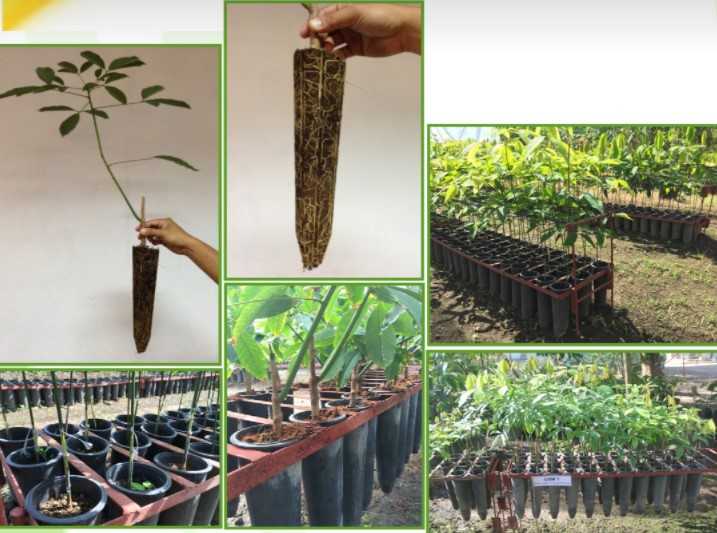
The Rubber ISP aims to address supply chain issues in the industry through various S&T interventions. These include varietal improvement and selection through barcoding of High Yielding Clones (HYCs), rapid clonal mass propagation techniques using root trainers in nursery production, and rapid mapping of existing plantations and suitable areas using Remote Sensing/Geographic Information System (RS/GIS). A computer-based Decision Support System (DSS) is used for species-site compatibility, alongside a Package of Technology (POT) for nursery and plantation management. The program also supports optimized rehabilitation techniques for senescent rubber trees through rubber-based agroforestry systems, Integrated Pest Management (IPM) using biocontrol agents and biopesticides, and enhanced rubber latex harvesting and coagulation techniques through the training of new rubber tappers and tapper trainers.
Strategic R&D
Strategic R&D is DOST-PCAARRD’s banner program comprising all R&D activities that are intended to generate outputs geared towards maximum economic and social benefits
White root rot (WRR) manifests conspicuously within regions 9, 10, and 12. Healthy root specimens were collected and subjected to laboratory processing to facilitate the...
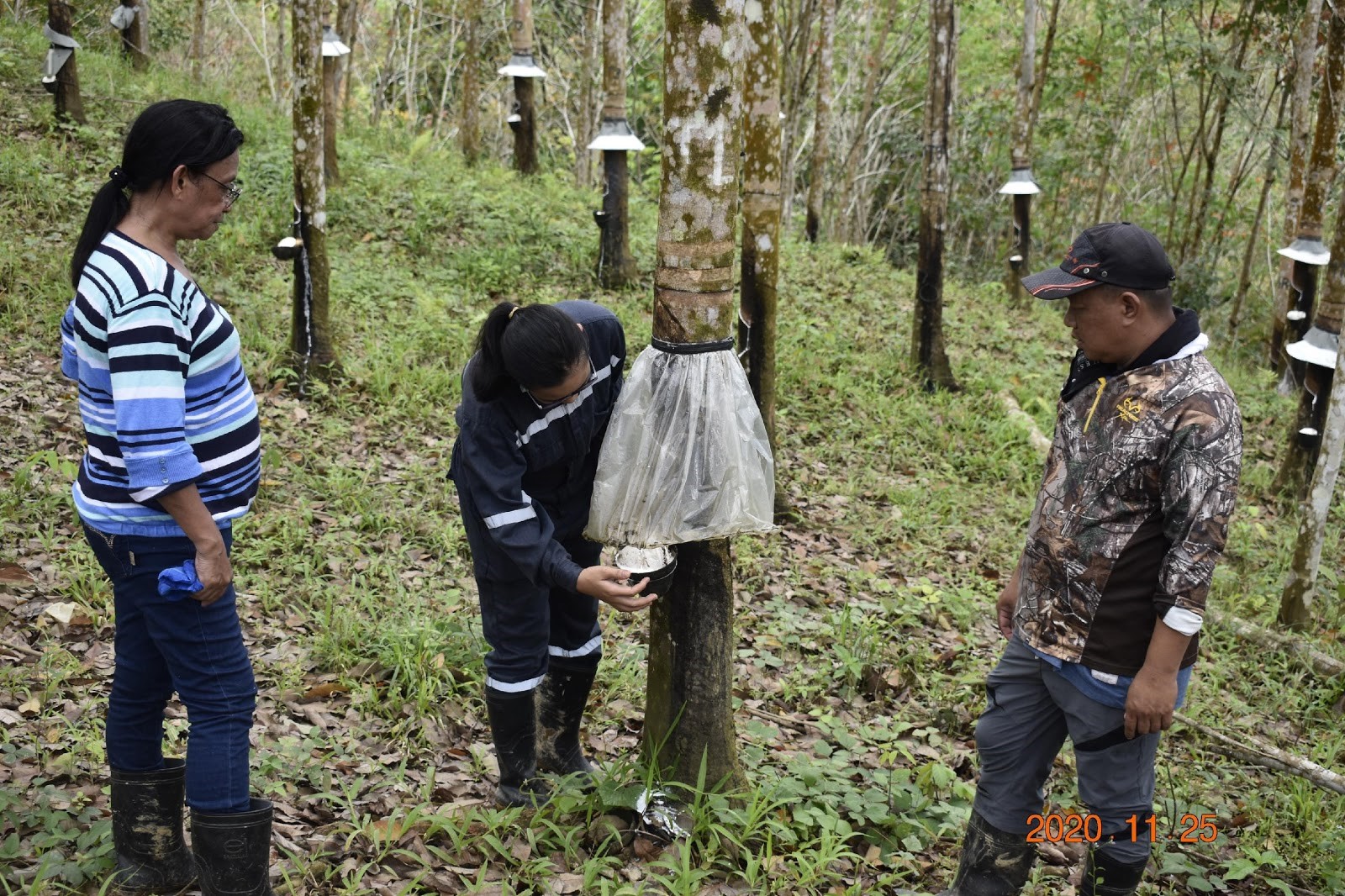
New PRRI Rubber Tapping Device with a replaceable blade Nowadays, latex harvesting is critical in rubber plantations. The tapping knife and tapping skills of the...
A quarter (¼) spiral upward tapping cut measured from 1.10m height above the ground with tapping angle of 450 and expected rubber lifespan of up...
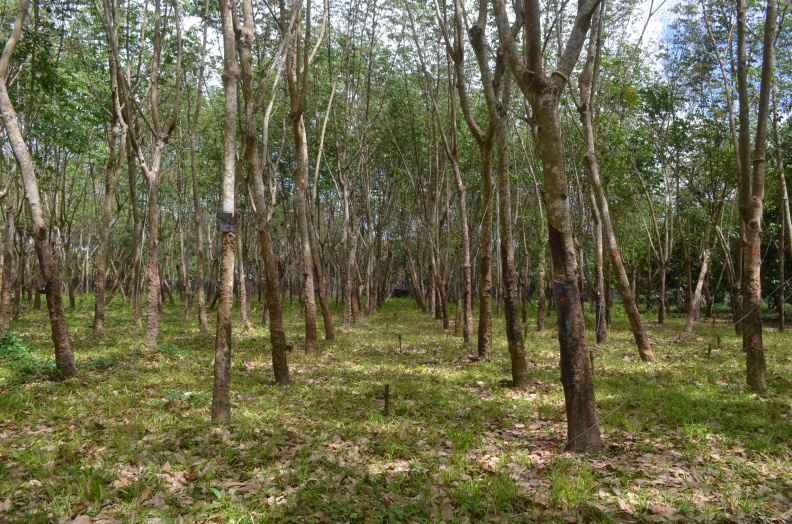
Rubber plantation in Sta. Maria Laguna Rubber Plantation in Sofronio Española, Palawan Rubber nursery (left) and budwood garden (right) in Bayawan, Negros Oriental Rubber production...
Tapping Panel DrynessStem bleeding Disease The study explored the factors involved in the development of Tapping Panel Dryness (TPD) and Stem Bleeding (SB) in rubber...
Identification of potential expansion areas for rubber is essential to increase local production and improve their quality while taking advantage of the market demand. A...
The program aimed to evaluate the adaptation and performance of recommended and other promising rubber clones in the Philippines in six different locations: (1) University...
Functional genomics involves studies on how genes and intergenic regions of the genome contribute to different biological processes. This is translated to the development of...
Technologies
Products, equipment, and protocols or process innovations developed to improve productivity, efficiency, quality, and profitability in the agriculture and aquatic industries, and to achieve sustainable utilization and management of natural resources
- Published On: November 26, 2021
Species-site compatibility is a crucial factor in the establishment of forest plantations (ERDB, 2010). In the past, species trials conducted showed that different species have...
- Published On: November 26, 2021
One aspect of growth improvement in rubber plants is in the good root development. For better growth of rubber seedlings, root trainer technology has been...
- Published On: November 26, 2021
Rubber is one of the top agricultural crops in the Philippines for it generates employment in the rural areas, enhances environmental rehabilitation in idle lands...
Technology Transfer Initiatives
Technology Transfer initatives ensure that the outputs of R&D and innovations are transformed into viable and applicable technologies that help intended users.
The project aims to strengthen the capacity of the Intellectual Property and Technology Business Development Office (IP-TBM) of the University of Southern Mindanao through patent...
Basilan is now identified as a centre of commercial crops in the ARMM. It is an opportunity to enhance the province’s potential for agricultural development....
This project will adopt existing rubber technology to be implemented by the College of Forestry and Natural Resources with the collaboration of the Southern Tagalog...
The intent of this project is to help improve the yield and quality of Philippine rubber latex and address the concern raised on incorrect tapping...
Zamboanga del Norte shared 4% of the country's total rubber production in 2010 where most of the rubber plantations are managed by Agrarian Reform Communities...
SOCCSKSARGEN, Cotabato is one of the top cup lump-producing provinces with a production of 173,110.31bmt in 2014 (PSA, 2014). Around 54,508.8 hectares are planted to...
Capacity Building
Capacity building efforts of DOST-PCAARRD seek to develop and enhance the R&D capabilities of researchers and academic or research institutions through graduate assistantships, non-degree trainings & development, and/or upgrading of research facilities.
Manpower Development
Policy Research & Advocacy
Analysis of policy concerns and advocacy of science-informed policies ensures that the AANR policy environment is conducive for S&T development and investments.

Policy Analysis and Advocacy on the Use of Various Latex Coagulants and Nano-Sensor for Improved Quality of Raw Rubber Products
In Western Mindanao, rubber is an important industry contributing significantly to the region with 40% of the total production area, 45% of dry rubber, and 42% of cup lump production. However, one critical issue affecting the industry is the use of battery solution instead of formic acid to increase weight, which leads to a lower dry rubber content in the coagulum and reduced quality of crumb rubber.
To address the issue of rubber quality detection, Surface Toughness Analyzer for Rubber (STAR) was developed. However, at field validation, it cannot detect the quality of rubber inside the block because of the shortness of probe. Additionally, it could only detect the type of acid used within a limited time frame of 7 to 30 days only.
The study recommends the following: (1) improvement of the STAR gadget for utilization, (2) make available ready to use formic acid to small farmers, (3) explore and increase local consumption of rubber-based products such as rubberize roads, (4) adopt schemes of issuing licenses to operate for farmer-producer, traders, and processors, (5) adopt good agricultural practices (GAP) and good manufacturing practices (GMP) as basis for exporting rubber products, and (6) consider the imposition of rubber levy to key players in the industry as fund for rubber development in the country.
Reference(s):
Based on the results of the PCAARRD funded project: Policy Analysis and Advocacy on the Use of Various Latex Coagulants and Nano-Sensor for Improved Quality of Raw Rubber Products. By Narvaez, T. (WMSU).