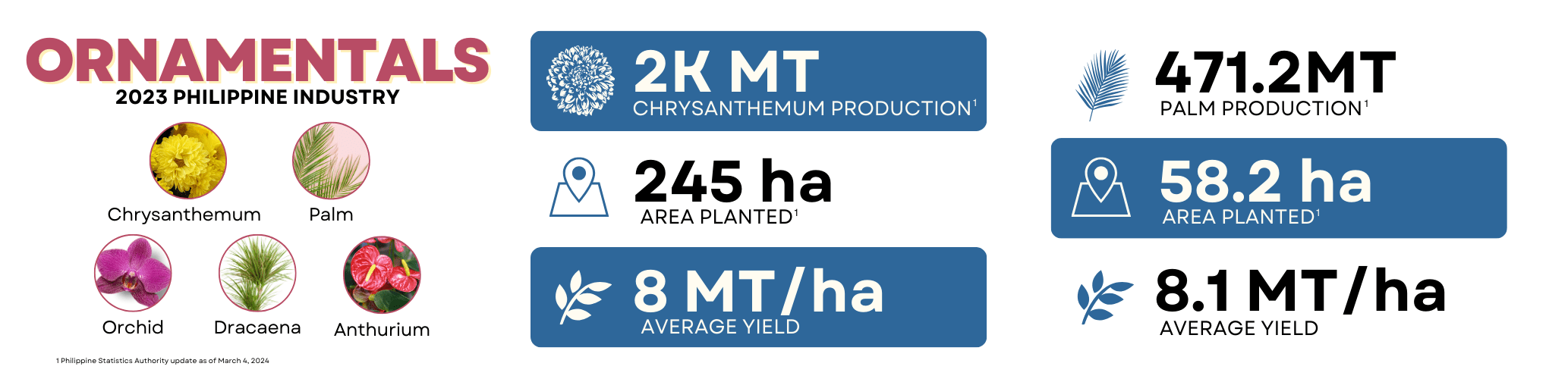
Industry Profile
Ornamentals are categorically classified into cutflowers, foliage, plant parts, live plants, and dried flowers and plants. The most popular cutflower cultivars produced in the Philippines include orchids, anthuriums, roses, gladioli, heliconias, and chrysanthemums. These flowers are commonly arranged in various forms such as corsages, wreaths, and other creative designs. Important foliage plants grown in the country include ferns, palms, podocarpus, crotons, dracaenas, and murrayas (Lantican, 2000).
The ornamental plants industry, dubbed as a “bright sunshine industry,” has encountered a multitude of opportunities and challenges. Initially, it began as a small-scale or backyard operation in the early 70s and commercial production in mid 80s when few growers ventured into business. The industry rapidly expanded in the 1990s with the entry of more commercial growers.
Problems in the Industry
The industry is affected by the following issues/concerns:
- Insufficient number of available planting materials;
- Lack of new and unique varieties of flowering and foliage ornamental plants with high acceptability for local and global markets;
- Lack of improved propagation/production protocols; pest and disease management control; policy recommendations.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Ornamentals Policies
ISP for Ornamentals
DOST-PCAARRD’s ISP for Ornamental Plants focuses on 11 priority commodities (Orchid, Hoya, Chrysanthemum, Anthurium, Hibiscus, and Adenium for flowering plants; and Dracaena, Cordyline, Palm, Aglaonema, and Alocasia for foliage plants). The ISP is directed to ensure the country’s supply of locally and globally-competitive ornamental plants by increasing its production, and establishing adequate post-production facilities and technologies.