Mangrove Crab
Industry Strategic Science and Technology Program
Mangrove Industry Profile
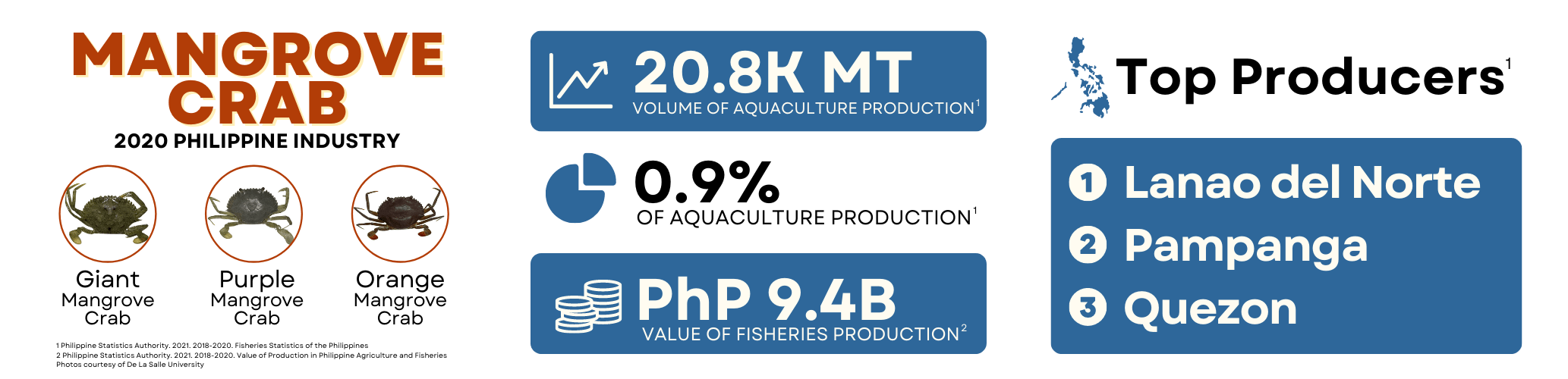
Mangrove crab, locally known as alimango, is the Philippines’ 6th most cultured species in terms of aquaculture production in 2020. Moreover, the Philippines remains to be one of the top producers of mangrove crab in the world. In 2020, PSA reported the Philippines’ total mangrove crab production at 20,766.25 MT. Northern Mindanao is the leading region with 7,759.36 MT, of which 6,812.38 MT came from the province of Lanao del Norte. Other notable provinces, with over 4,000 MT mangrove crab production each are Pampanga and Quezon. The three known species of mangrove crab in the Philippines are Scylla serrata, S. tranquebarica, and S. olivacea. They are distinguished by color patterns, relative size, spines, chromosome form, gamete development, and preferred habitats. In 2021, the average price of mangrove crab is Php 395.94 per kilogram.
The Philippine mangrove crab production is undertaken using polyculture systems in 30% of brackishwater fishponds in the country. The industry is estimated to require 36-45 million crablets annually, which currently is sourced out from the wild.
Problems in the Industry
The Philippines has been a pioneer in developing the basic technology for mangrove crab hatchery. However, the supply of broodstock is still inadequate for hatchery production which results to inadequate supply of crablets/juveniles for grow-out culture. Thus, mangrove crab production is still dependent on the supply of wild-caught crablets.
The commercialization of the hatchery technology is constrained by the high production cost, low survival in nurseries due to cannibalism and diseases, lack of low-cost and practical artificial diets and use of banned and unregulated drugs for disease control.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Mangrove Crab Policies
| Policy Type | Policy Number | Policy Year | Congress | Policy Title | Policy Description | Policy Objective | Policy Link | Commodity | Classification | info_encoder_stamp | info_date_stamp | info_quashing_remarks | filepath |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Order | Fisheries Administrative Order No. 264-1 | 2023 | Null | Amending Fisheries Administrative Order No. 264, Series Of 2020, Entitled "Regulation On The Catching, Possession, Transporting, Selling, Trading And Exporting Of Mangrove Crablets, Juvenile Mangrove Crabs And Gravid Mangrove Crabs (Scylla spp.)" | WHEREAS, Fisheries Administrative Order No. 264 series of 2020 (FAO 264) was issued as a measure to curve the unregulated gathering of mangrove crab instar to crablets size for aquaculture and to protect the wild population of mangrove crabs. However, it was envisioned that the mangrove crab hatchery industry would increase its capacity to cater to the need for grow-out aquaculture; WHEREAS, reports from concerned BFAR technical centers show that the current capacity of mangrove-crab hatcheries in the country can only supply less than 10% of the instar crab requirement for grow-out aquaculture. The industry is still widely considered as capture/wild-based aquaculture. Thus, the NFRD I and other relevant academic and research institutions are promoting other developmental strategies such as nursery-rearing technology of wild instar (fly-size) mangrove crabs; WHEREAS, the effect of FAO 264 is also evident in the export trade of live mangrove crabs which has significantly decreased due to its implementation; WHEREAS, regulations should still be in place pursuant to Section 104 of Republic Act No. 8550, as amended by Republic Act No. 10654 (the Amended Fisheries Code), which states that "Exportation of breeders, spawners, eggs or fry as prohibited in this Code shall be punished under this Act: Provided, That the export of hatchery-bred or captive-bred breeder, spawner, egg or fry, may be allowed subject to the regulations to be promulgated by the Department"; | This order seeks to amend the Fisheries Administrative Order No. 264, series of 2020. Fisheries Administrative Order No. 264 series of 2020 (FAO 264) was issued as a measure to curve the unregulated gathering of mangrove crab instar to crablets size for aquaculture and to protect the wild population of mangrove crabs. However, it was envisioned that the mangrove crab hatchery industry would increase its capacity to cater to the need for grow-out aquaculture. | https://www.bfar.da.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/FAO-2023-264-1-dated-December-11-2023.pdf | Mangrove Crab | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Mangrove_Crab_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Republic Act | Republic Act 11911 | 2021 | 18th | An Act Establishing A Mangrove Crab Hatchery In Barangay Geratag, Municipality Of San Jose, Province Of Northern Samar, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | SECTION 1. There shall be established, under the supervision of the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources of the Department of Agriculture (BFAR-DA), a mangrove crab hatchery in Barangay Geratag, Municipality of San Jose, Province of Northern Samar. SEC. 2. Prior to the establishment of the mangrove crab hatchery, the BFAR- DA shall conduct a full-scale feasibility study in support of its construction to comply with the requirements of the Department of Budget and Management. Within two (2) years after the construction of the mangrove crab hatchery, the BFAR-DA, through a memorandum of agreement, shall transfer its management to the local government of the Municipality of San Jose . It shall implement a training and phasing-in program for local government personnel on the management and operation of the hatchery. SEC. 3. The BFAR- DA shall conduct continuing research and experimentation on the breeding and production of mangrove crab species, especially as they apply to local conditions, to discover new methods and technologies that will enhance the fishing industry. SEC. 4. The Secretary of Agriculture shall include in the Department's programs the conduct of the feasibility study and the consequent establishment of the mangrove crab hatchery in Barangay Geratag, Municipality of San Jose, Province of Northern Samar, the funding of which shall be included in the General Appropriations Act. The local government unit concerned shall set aside funds from any available local revenue in an amount deemed appropriate for the operationalization of the hatchery. | This Act aims to establish a mangrove crab hatchery in barangay Geratag, municipality of San Jose in the Province of Northern Samar. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/ra_18/RA11911.pdf | Mangrove Crab | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Mangrove_Crab_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Order | Fisheries Administrative Order No. 264 | 2020 | Null | Regulation On The Catching, Possession, Transporting, Selling, Trading And Exporting Of Mangrove Crablets, Juvenile Mangrove Crabs And Gravid Mangrove Crabs (Scylla spp.) | WHEREAS, Section 2(c) of the Republic Act No. 8550 as amended by RA No. 10654 provides for the rational and sustainable development, management and conservation of the fishery and aquatic resources in Philippine waters including the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and in the adjacent high seas, consistent with the primordial objective of maintaining a sound ecological balance, protecting and enhancing the quality of the environment; WHEREAS, gathering of mangrove crablets to megalopa stage from the wild for aquaculture and exportation purposes had gone rampant and unregulated over the years, which may lead to stock depletion and growth overfishing; WHEREAS, the three most common species of mangrove crabs in the Philippines are Scylla serrata, S. tranquebarica and S. olivacea. The S. serrata is the most prominent in aquaculture industry, the seeds/crablets of whcih are mainly collected from the wild; WHEREAS, some areas in Northern Luzon, Bicol region, Eastern Visayas, Northern Mindanao, Caraga region, and Zamboanga region have already adopted regulations on gathering and trading of Mangrove crablets, including the prohibition on the collection and transport of "langaw-langaw" from the wild; WHEREAS, studies showed that high mortality is evident during collection and transport of fly-size mangrove crabs. Furthermore, push net or scissor are being used as the primary collection method. These collection methods catch juvenile of other species and contributes to environmental damage; | This order aims to curve the unregulated gathering of mangrove crab instar to crablets size for aquaculture and to protect the wild population of mangrove crabs. | https://www.bfar.da.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/FAO-No.-264-s.-2020.pdf | Mangrove Crab | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Mangrove_Crab_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Republic Act | Republic Act 10857 | 2015 | 16th | An Act Establishing Mangrove Crab Seed Banks, Nurseries And Grow-Out Production Farms In The Municipalities Of Virac, Bato, Baras, Gigmoto, Viga, Panganiban, Bagamonoc, San Andres, Caramoran And Pandan, Province Of Catanduanes And Appropriating Funds Therefor | SECTION 1. There shall be established, under the supervision of the Department of Agriculture, mangrove crab seed banks, nurseries and grow-out production farms in the municipalities·of Virac, Bato, Baras Gigmoto,Viga, Panganiban, Bagamanoc, San Andres, Caramoran and Pandan, Province of Catanduanes. SEC. 2. The Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources (BFAR), the Provincial Government of Catanduanes, the concerned local government units (LGUs), and the Catanduanes State University shall, in the identification of areas where these seed banks, nurseries and grow-out production farms will be established shall place priority to the utilization of abandoned, undeveloped or underutilized fishponds covered by fishpond lease agreements. SEC. 3.The BFAR and the Provincial Government of Catanduanes, in collaboration with the Catanduanes State University, shall issue guidelines and provide technical assistance to fishermen and .their association, in the establishment, operation, maintenance, supervision and monitoring of mangrove crab seed banks, nurseries and grow-out production farms. SEC. 4.The Secretary of Agriculture shall include in the Department's programs the establishment of the mangrove crab seedbanks, nurseries and grow-out production farms, the funding of which shall be included in the annual General Appropriations Act. The LGUs concerned shall set aside funds from any available local revenue to fund their establishment, supervision and monitoring. | This act aims to establish mangrove crab seed banks, nurseries and grow-out production farms in the municipalities of Virac, Bato, Baras, Gigmoto, Viga, Panganiban, Bagamonoc, San Andres, Caramoran and Pandan in the province of Catanduanes | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/ra_16/RA10857.pdf | Mangrove Crab | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Mangrove_Crab_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx |
ISP for Mangrove Crab
The ISP for mangrove crab aims to refine existing protocols for mangrove crab hatchery, nursery and grow-out, and to demonstrate feasibility and viability of commercial mangrove crab hatcheries. The target outcomes are increased survival rate in hatchery, nursery, and grow-out, and to establish a sustainable mangrove crab production.
Strategic R&D
Strategic R&D is DOST-PCAARRD’s banner program comprising all R&D activities that are intended to generate outputs geared towards maximum economic and social benefits
Fattening of crabs is an easy-to-learn technology and can be a good means of improving the livelihood of coastal communities because it is profitable and...
The use of biotechnology specifically focusing on the metabolic pathways and metabolites (biogenic amines and terpenoids) directly involved with molting presents itself as an intuitive...
The program titled “Harnessing emerging technologies for mangrove crab culture and resource management: ‘omics approaches, web-based and mobile computing technologies” is composed of the following...
This program used high throughput DNA sequencing methods to generate novel SNP markers for stock delineation and traceability of natural populations of mangrove crabs. It...
The program titled “Program D. Disease Management for Improved Mud Crab Production” is composed of the following projects:Project 1. Novel strategies to reduce disease incidence...
The program titled “Program C. Improvement of Feeds and Stock Management Practices for Mud Crab Grow-out Culture” is composed of the following projects: Project 1. ...
The program titled “Program B. Refinement of Mud Crab Nursery Technology” is composed of the following projects: Project 1. Refinement of efficient diets for nursery cultureProject...
The program titled “Program A. Refinement of Mud Crab Hatchery Technology” is composed of the following projects: Project 1. Development of techniques for mass production of...
Technologies
Products, equipment, and protocols or process innovations developed to improve productivity, efficiency, quality, and profitability in the agriculture and aquatic industries, and to achieve sustainable utilization and management of natural resources
A project titled “A rapid cost-effective method to screen potential sources of immunostimulants and growth promoting feed additives for Scylla serrata using a functional genomics...
A project on Improvement of larval rearing hatchery under the program Refinement of Mud Crab Hatchery Technology was implemented to address the issues such as...
Of the three mangrove crab species in the Philippines, Scylla serrata, or the giant mangrove crab, is capable of growing faster and bigger compared to...
Technology Transfer Initiatives
Technology Transfer initatives ensure that the outputs of R&D and innovations are transformed into viable and applicable technologies that help intended users.
- Published On: June 10, 2022
The project will be implemented in Alaminos City, Pangasinan wherein a turn key arrangement will be forged by PSU with the Municipal LGU. With the...
Capacity Building
Capacity building efforts of DOST-PCAARRD seek to develop and enhance the R&D capabilities of researchers and academic or research institutions through graduate assistantships, non-degree trainings & development, and/or upgrading of research facilities.
Infrastructure Development
Manpower Development
Policy Research & Advocacy
Analysis of policy concerns and advocacy of science-informed policies ensures that the AANR policy environment is conducive for S&T development and investments.

Improving the Supply Chain of Mudcrab in the Philippines: The Case of Central Luzon
The study notes that key players are able to fulfill the obligations and responsibilities expected from them, especially in meeting the volume requirement for the other chain members to properly operate. In certain occasions, the consignacion even acts as a bidder in the bulungan to meet the number of mudcrab needed by exporters. The level of trust among trading partners, as they have been working with each other for several years, was discovered to generate a market situation where efficiency and effectiveness is not fully compromised.
Still, various inefficiencies were observed in the supply chains. Occasional crablet shortage, crablet delivery delays, and distant source areas of crablets greatly add to the transaction costs on the part of mudcrab growers. While the bulungan system was observed to work in completing the transactions, it was also noted as an inaccurate way of price determination given its dependency on the buyer’s willingness to pay. Other issues enumerated in the study include the lack of financial resources of mudcrab growers and traders, as well as external factors such as unfavorable weather conditions, flooding, typhoons, and water pollution.
Reference(s):
Porciuncula, F.L., Padilla, J.N., Saturno, J.O., and Parayno, R.S. (2014). Supply Chain Improvement of Mudcrab in Central Luzon Region (Phase 1: Evaluation Research). Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: Philippine Council for Agriculture, Aquatic and Natural Resources Research and Development – (Project Report)