Tilapia
Industry Strategic Science and Technology Program
Tilapia Industry Profile
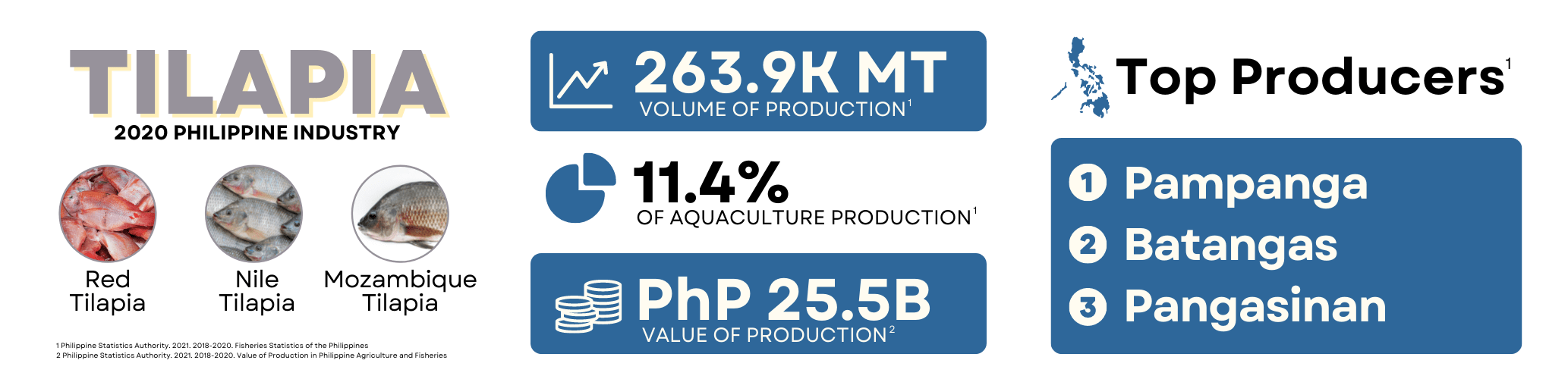
Tilapia is the second most important cultured species in the country accounting for 281,111 MT total production in 2021. Philippines’ total production was 263,871 MT in 2020, which makes up 20% of the Philippines’ aquaculture production, with Central Luzon as the leading region with tilapia production of 136,218 MT. The most common species is the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), or gray tilapia, which has several improved breeds available from government and private hatcheries. It can tolerate brackishwater with salinities of up to 25 parts per thousand (ppt). Tilapia is an important commodity for food security because it is widely accepted and is suitable for mass production through grow-out culture in backyard and commercial scale.
Tilapia fry produced in breeding units are kept in the nursery unit until fingerling size before moving them into grow-out units to ensure proper growth of the fish and good survival rate. Fish need adequate space, food, and a healthy environment so it is important to consider water depth, food supply, and water quality in determining how many fish are kept in the same area.
In the Philippines, tilapia is produced mainly for local consumption. The produce can be sold fresh, chilled, or live. When grown to large size and fileted, tilapia can also be marketed as a premium white fish as its mild tasting lean flesh is flaky for its somewhat firm texture. Some places in the country, smoking of tilapia is done but mainly for the immediate locality.
Problems in the Industry
The problems faced by the Philippine Tilapia industry include:
For freshwater tilapia strains:
- Low survival rate (averaging 55%) in typical freshwater grow-out farm compared to modern farm
- Mass mortalities arising from poor culture conditions and disease outbreaks
- Non/slow adoption of good aquaculture practices and technologies
- Quality source of breeders and fry
For saline tilapia strains:
- Low survival rate of saline tilapia in brackishwater ponds
- Low production of tilapia in brackishwater and marine waters
- Slow growth of saline tilapia strain in brackishwater ponds
- No aquaculture of saline tilapia in estuarine mangrove environment
- Quality source of breeders and fry to meet the expansion of the industry
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Tilapia Policies
| Policy Type | Policy Number | Policy Year | Congress | Policy Title | Policy Description | Policy Objective | Policy Link | Commodity | Classification | info_encoder_stamp | info_date_stamp | info_quashing_remarks | filepath |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bill | House Bill No. 6793 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of Asingan, Province Of Pangasinan | People in the Municipality of Asingan generally rely on agriculture for their livelihood, particularly the cultivation of rice, corn, and assorted vegetables. As such, the supply of fish and other aquatic resources for their important dietary needs is far from ideal resulting in its price becoming quite prohibitive for many of its people. Given this situation, the establishment of the above-mentioned multi-purpose fishery farm in the Municipality of Asingan, Province of Pangasinan will greatly benefit its people. Its creation will timely meet the increasing demand of people in the said Municipality for affordable fish. It will also provide, for its people, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the setting up, management, and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading up to the empowerment of many of its people and the creation of secondary income streams for them which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of Asingan, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes which are viable in mud ponds and concrete tanks in the Municipality of Asingan, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06793.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6794 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of Balungao, Province Of Pangasinan | Balungao is a land-locked municipality, some areas of which are hilly, and many of its communities rely mostly on agriculture, particularly the cultivation of rice, corn, and assorted vegetables. Fish is integral to a healthy staple food for everyone, along with rice, meat, fruits and vegetables. However, its supply in this Municipality is limited and the price quite expensive for many of its people. And so, the creation of the proposed multi-purpose fishery farm in Balungao presents a viable solution to the scarcity of this aquatic commodity, and will timely meet the increasing demand of people for it. It will provide, for its communities, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the setting up, management, and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading up to the empowerment of many people in these communities and the creation of secondary income streams which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of Balungao, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes which are viable in concrete tanks and mud ponds in the Municipality of Balungao, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06794.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6795 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of Natividad, Province Of Pangasinan | People in the Municipality of Natividad generally rely on agriculture for their livelihood, particularly the cultivation of rice, corn, and assorted vegetables. As such, the supply of fish and other aquatic resources for their important dietary needs is far from ideal resulting in its price becoming quite prohibitive for many of its people. Given this situation, the establishment of the above-mentioned multi-purpose fishery farm in the Municipality of Natividad, Province of Pangasinan will greatly benefit its people. Its creation will timely meet the increasing demand of people in the said Municipality for affordable fish. It will also provide, for its people, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the setting up, management, and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading up to the empowerment of many of its people and the creation of secondary income streams for them which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of Natividad, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry. | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes which are viable in mud ponds and concrete tanks in the Municipality of Natividad, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06795.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6796 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of Rosales, Province Of Pangasinan | Rosales is a land-locked municipality, and many of its communities rely mostly on agriculture, particularly the cultivation of rice, corn, and assorted vegetables. Fish is integral to a healthy staple food for everyone, along with rice, meat, fruits and vegetables. However, its supply in this locality is limited, thereby making the price a quite expensive. And so, the creation of the proposed multi-purpose fishery farm in Rosales presents a viable solution to the scarcity of this aquatic commodity, and will timely meet the increasing demand of people for it. It will provide, for its communities, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the setting up, management, and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading up to the empowerment of many people in these communities and the creation of secondary income streams which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of Rosales, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry. | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes which are viable in concrete tanks and mud ponds in the Municipality of Rosales, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06796.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6797 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of San Manuel, Province Of Pangasinan | People in the Municipality of San Manuel generally rely on agriculture for their livelihood, particularly the cultivation of rice, corn, and assorted vegetables. As such, the supply of fish and other aquatic resources for their important dietary needs is far from ideal. It is in this context that the establishment of the above-mentioned multi-purpose farm in the Municipality of San Manuel, Province of Pangasinan is being proposed. It is hoped that its creation will timely meet the increasing demand of people in the said Municipality for affordable fish. It will also provide, for its people, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the care and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading to their empowerment and the creation of secondary income streams which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of San Manuel, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes which are viable in mud ponds and concrete tanks in the Municipality of San Manuel, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06797.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6798 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of San Nicolas, Province Of Pangasinan | Majority of people in the Municipality of San Nicolas generally rely on agriculture for their livelihood, particularly the cultivation of rice and assorted vegetables. As such, the supply of fish and other aquatic resources for their important dietary needs is far from ideal. It is in this context that the establishment of the above-mentioned multi-purpose farm in the Municipality of San Nicolas, Province of Pangasinan is being proposed. It is hoped that its creation will timely meet the increasing demand of people in the said Municipality for affordable fish. It will also provide, for its people, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the care and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading to their empowerment and the creation of secondary income streams which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of San Nicolas, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry. | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes in the Municipality of San Nicolas, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06798.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6799 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of San Quintin, Province Of Pangasinan | A substantial part of the population in the Municipality of San Quintin generally rely on agriculture for their livelihood, particularly the cultivation of rice, corn, and assorted vegetables. As such, the supply of fish and other aquatic resources for their important dietary needs is far from ideal. It is in this context that the establishment of the above-mentioned multi-purpose farm in the Municipality of San Quintin, Province of Pangasinan is being proposed. It is hoped that its creation will timely meet the increasing demand of people in the said Municipality for fish. It will also provide, for its people, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the care and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading to their empowerment and the creation of secondary income streams which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of San Quintin, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry. | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes in the Municipality of San Quintin, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06799.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6800 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of Santa Maria, Province Of Pangasinan | Santa Maria is a land-locked municipality, and many of its communities rely mostly on agriculture, particularly the cultivation of rice, corn, and assorted vegetables. Fish, which is integral to a healthy staple food for everyone, along with rice, meat, fruits and vegetables, is scarce and expensive in this locality. And so, the creation of the proposed multi-purpose farm in Santa Maria presents a viable solution to the scarcity of, and will timely meet the increasing demand for, this aquatic commodity in this Municipality. It will provide, for its communities, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the care and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading to the empowerment of many people in these communities and the creation of secondary income streams which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of Santa Maria, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry. | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes which are viable in concrete tanks and mud ponds in the Municipality of Santa Maria, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06800.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6801 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of Tayug, Province Of Pangasinan | Tayug is a land-locked municipality and many of its communities rely mostly on agriculture, particularly the cultivation of rice and assorted vegetables. Fish, which is integral to a healthy staple food for everyone, along with rice, meat, fruits and vegetables, is scarce and expensive in this locality. And so, the creation of the proposed multi-purpose farm in Tayug presents a viable solution to the scarcity of, and will timely meet the increasing demand for, this aquatic commodity in the Municipality of Tayug. It will provide, for its communities, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the care and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading to the empowerment of many people in these communities and the creation of secondary income streams which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of Tayug, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes which are viable in concrete tanks and mud ponds in the Municipality of Tayug, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06801.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 6802 | 2023 | 19th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Purpose Farm For The Breeding, Spawning, And Hatchery Of Catfish, Tilapia, Mudfish, Eel, And Other Fresh Water Fishes In The Municipality Of Umingan, Province Of Pangasinan | Umingan is a land-locked municipality, a good portion of which is hilly, and many of its communities rely mostly on agriculture, particularly the cultivation of rice and assorted vegetables. Fish, which is integral to a healthy staple food for everyone, along with rice, meat, fruits and vegetables, is scarce and expensive in this locality. And so, the creation of the proposed multipurpose farm in Umingan presents a viable solution to the scarcity of, and will timely meet the increasing demand for, this aquatic commodity in this Municipality. It will provide, for its communities, a stable source of fry or fingerlings as well as reliable technical expertise for the care and operation of small-scale fish farms; thereby, ultimately leading to the empowerment of many people in these communities and the creation of secondary income streams which will augment their incomes from agriculture. This proposed bill, although local in its scope and application, will eventually redound to nation-building, as it will provide a viable source of livelihood for people in the rural areas of Umingan, and eradicate poverty subsisting therein, particularly in far-lung communities. Moreover, it will also help in the rejuvenation of the fish industry. | This bill seeks to establish a multi-purpose farm for the breeding, spawning, and hatchery of catfish, tilapia, mudfish, eel, and other fresh water fishes which are viable in concrete tanks and mud ponds in the Municipality of Umingan, Province of Pangasinan. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_19/HB06802.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Republic Act | Republic Act No. 11778 | 2021 | 18th | An Act Establishing A Technology Verification Station With Tilapia And Freshwater Prawn Hatcheries In The Municipality Of Sto. Domingo, Province Of Nueva Ecija, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | SECTION 1. There shall be established, under the supervision of the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources of the Department of Agriculture (BFAR-DA), a technology verification station with tilapia and freshwater prawn hatcheries in the Municipality of Sto. Domingo, Province of Nueva Ecija. SEC. 2. Prior to the establishment of the technology verification station with tilapia and freshwater prawn hatcheries, the BFAR-DA shall conduct a full-scale feasibility study in support of its construction to comply with the requirements of the Department of Budget and Management. Within two (2) years after the construction of the technology verification station with tilapia and freshwater prawn hatcheries, the BFAR-DA, through a memorandum of agreement, shall transfer its management to the local government of the Municipality of Sto. Domingo. It shall implement a training and phasing-in program for local government personnel on the management and operation of the technology verification station and hatcheries. | This aims to establish a technology verification station with tilapia and freshwater prawn hatcheries in the municipality of Sto. Domingo, Province of Nueva Ecija. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2022/05/27/republic-act-no-11778/ | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 10309 | 2021 | 18th | An Act Establishing A Technology Verification Station With Bangus, Tilapia And Freshwater Prawn Hatcheries In The Coastal Municipality Of Hagonoy, Province Of Bulacan, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | According to the statistics provided by Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources III, Bulacan contributed 15% or 6,222.16MT of the Aquaculture sector share to the total provincial fisheries production of 41,418.05MT. Major Aquaculture Species in the Province of Bulacan are bangus, tilapia, sugpo, mudcrab, catfish, oyster and mussel. Of the total aquaculture production, bangus is the top contributor followed by tilapia and sugpo. This industry is established and is already contributing to the province’s economy. If we can develop and harness the potential economic contribution and impact of this natural resources, it can jumpstart the abrupt halt in the Philippine’s economic growth brought by the pandemic. | This bill aims to establish a technology verification station with major aquaculture species hatcheries in the coastal Municipality of Hagonoy, Province of Bulacan. This measure will boost the already flourishing industry of fisheries production and will provide employment and business opportunities this pandemic. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_18/HB10309.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 10310 | 2021 | 18th | An Act Establishing A Technology Verification Station With Bangus, Tilapia And Freshwater Prawn Hatcheries In The Coastal Municipality Of Obando, Province Of Bulacan, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | According to the statistics provided by Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources III, Bulacan contributed 15% or 6,222.16MT of the Aquaculture sector share to the total provincial fisheries production of 41,418.05MT. Major Aquaculture Species in the Province of Bulacan are bangus, tilapia, sugpo, mudcrab, catfish, oyster and mussel. Of the total aquaculture production, bangus is the top contributor followed by tilapia and sugpo. This industry is established and is already contributing to the province’s economy. If we can develop and harness the potential economic contribution and impact of this natural resources, it can jumpstart the abrupt halt in the Philippine’s economic growth brought by the pandemic. | This aims to establish a technology verification station with major aquaculture species hatcheries in the coastal Municipality of Obando, Province of Bulacan. This measure will boost the already flourishing industry of fisheries production and will provide employment and business opportunities this pandemic. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_18/HB10310.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 10311 | 2021 | 18th | An Act Establishing A Technology Verification Station With Bangus, Tilapia And Freshwater Prawn Hatcheries In The Coastal Municipality Of Paombong, Province Of Bulacan, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | According to the statistics provided by Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources III, Bulacan contributed 15% or 6,222.16MT of the Aquaculture sector share to the total provincial fisheries production of 41,418.05MT. Major Aquaculture Species in the Province of Bulacan are bangus, tilapia, sugpo, mudcrab, catfish, oyster and mussel. Of the total aquaculture production, bangus is the top contributor followed by tilapia and sugpo. This industry is established and is already contributing to the province’s economy. If we can develop and harness the potential economic contribution and impact of this natural resources, it can jumpstart the abrupt halt in the Philippine’s economic growth brought by the pandemic. | This bill aims to establish a technology verification station with major aquaculture species hatcheries in the coastal Municipality of Paombong, Province of Bulacan. This measure will boost the already flourishing industry of fisheries production and will provide employment and business opportunities this pandemic. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_18/HB10311.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 10312 | 2021 | 18th | An Act Establishing A Technology Verification Station With Bangus, Tilapia And Freshwater Prawn Hatcheries In The Coastal Municipality Of Bulakan, Province Of Bulacan, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | According to the statistics provided by Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources III, Bulacan contributed 15% or 6,222.16MT of the Aquaculture sector share to the total provincial fisheries production of 41,418.05MT. Major Aquaculture Species in the Province of Bulacan are bangus, tilapia, sugpo, mudcrab, catfish, oyster and mussel. Of the total aquaculture production, bangus is the top contributor followed by tilapia and sugpo. This industry is established and is already contributing to the province’s economy. If we can develop and harness the potential economic contribution and impact of this natural resources, it can jumpstart the abrupt halt in the Philippine’s economic growth brought by the pandemic. | This bill aims to establish a technology verification station with major aquaculture species hatcheries in the coastal Municipality of Bulakan, Province of Bulacan. This measure will boost the already flourishing industry of fisheries production and will provide employment and business opportunities this pandemic. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_18/HB10312.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 10313 | 2021 | 18th | An Act Establishing A Technology Verification Station With Bangus, Tilapia And Freshwater Prawn Hatcheries In The Coastal Municipality Of Calumpit, Province Of Bulacan, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | According to the statistics provided by Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources III, Bulacan contributed 15% or 6,222.16MT of the Aquaculture sector share to the total provincial fisheries production of 41,418.05MT. Major Aquaculture Species in the Province of Bulacan are bangus, tilapia, sugpo, mudcrab, catfish, oyster and mussel. Of the total aquaculture production, bangus is the top contributor followed by tilapia and sugpo. This industry is established and is already contributing to the province’s economy. If we can develop and harness the potential economic contribution and impact of this natural resources, it can jumpstart the abrupt halt in the Philippine’s economic growth brought by the pandemic. | This bill aims to establish a technology verification station with major aquaculture species hatcheries in the coastal Municipality of Calumpit, Province of Bulacan. This measure will boost the already flourishing industry of fisheries production and will provide employment and business opportunities this pandemic. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_18/HB10313.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 10314 | 2021 | 18th | An Act Establishing A Technology Verification Station With Bangus, Tilapia And Freshwater Prawn Hatcheries In The Coastal Municipality Of Malolos, Province Of Bulacan, And Appropriating Funds Therefor | According to the statistics provided by Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources III, Bulacan contributed 15% or 6,222.16MT of the Aquaculture sector share to the total provincial fisheries production of 41,418.05MT. Major Aquaculture Species in the Province of Bulacan are bangus, tilapia, sugpo, mudcrab, catfish, oyster and mussel. Of the total aquaculture production, bangus is the top contributor followed by tilapia and sugpo. This industry is established and is already contributing to the province’s economy. If we can develop and harness the potential economic contribution and impact of this natural resources, it can jumpstart the abrupt halt in the Philippine’s economic growth brought by the pandemic. | This bill aims to establish a technology verification station with major aquaculture species hatcheries in the coastal City of Malolos, Province of Bulacan. This measure will boost the already flourishing industry of fisheries production and will provide employment and business opportunities this pandemic. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_18/HB10314.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Order | Fisheries Administrative Order No. 205 | 2000 | Null | Price list of tilapia fingerlings and breeder and carp fingerlings for sale by the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources | SECTION I. Prescribed price list.- The price list of improved strains of tilapia fingerlings and broodstock and carp fingerlings for sale by t he Bureau of f isheries & Aquatic Resources shall be as follows: SPECIES/SIZE PRICE (per piece) a. Tilapia fingerlings ·(for grow-out purposes) Size 24 (0.02 - 0.2 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - P0. 15 Size 22 (0.21 - 0.42 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.25 Size 17 (0.56 - I.5 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.35 Size 14 ( l.6 - 3.2 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.45 b. Tilapia broodstock (for hatchery purposes) (0.02 - 3.2 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1.00 Common carp Size 24 (less than 0.5 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -0.17 Size 22 (0.5 - 0.9 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.20 Size l7 ( I - 1.9 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.30 Size 14 (2 - 5 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - .0.50 Major carps Size 24 (less than 0.5 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -0.26 Size 22 (0.5 - 0.9 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -0.30 Size17 (1-1.9 g) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -0.50 Size 14 (2 -5 g) - - -- - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - 1.00 SECTION 2. Repeal. - FAO No. 186, existing lists and administrative orders or parts thereof inconsistent herewith are hereby amended accordingly. | This order aims to provide the updated price list of tilapia fingerlings and breeder and carp fingerlings for sale by the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources. | https://www.bfar.da.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/FAO-No.-205-s.-2000.pdf | Tilapia | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Tilapia_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx |
ISP for Tilapia
The ISP interventions aim to ensure a steady supply of quality fingerlings, boost production using detection kits and oral fish vaccines, and expand tilapia farming into brackish water systems. Target outcomes include improved survival rates in both freshwater and saline tilapia grow-out cultures, certified hatcheries in Luzon (for freshwater) and in Visayas and Mindanao (for brackishwater), and the development of saline tilapia farming in estuarine mangrove areas.
Strategic R&D
Strategic R&D is DOST-PCAARRD’s banner program comprising all R&D activities that are intended to generate outputs geared towards maximum economic and social benefits
The Central Luzon State University through the leadership of Dr. Emmanuel M. Vera Cruz developed the aquashade for the tilapia hatchery production in 2016. Shading...
Among the various disease-causing pathogens, bacterial pathogens are the major cause of infections and disease problems in wild fish and fish reared in confined conditions....
The Central Luzon State University through the leadership of Dr. Juvy J. Monserate developed the Zeolite-silica Nanocomposite (ZNC) technology. The ZNC is a novel material...
The University of the Philippines through the leadership of Dr. Carmello del Castillo initiated the on-going project which started in the last quarter of 2020,...
The University of the Philippines through the leadership of Prof. Fredson Huervana initiated the on-going project which started in the last quarter of 2020, it...
Technologies
Products, equipment, and protocols or process innovations developed to improve productivity, efficiency, quality, and profitability in the agriculture and aquatic industries, and to achieve sustainable utilization and management of natural resources
- Published On: March 17, 2022
Hot temperatures, particularly during El Nino episodes can lower fry production in hatcheries by reducing the frequency of spawning and egg production. To...
- Published On: March 17, 2022
The Zeolite-silica nanocomposite (ZNC) is a novel material synthesized and fully characterized at the CLSU Nanotechnology R & D Facility. ZNC can be utilized as...
- Published On: March 17, 2022
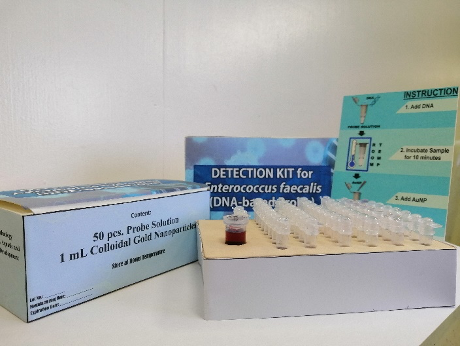
It is accurate, faster, user-friendly and convenient diagnosis using the developed detection kit, compared to the time consuming and lesser user-friendly conventional diagnosis. Farmers themselves...
Technology Transfer Initiatives
Technology Transfer initatives ensure that the outputs of R&D and innovations are transformed into viable and applicable technologies that help intended users.
- Published On: June 10, 2022
This project will involve an interdisciplinary team who will work for wider adoption of the technology in Luzon where most of the tilapia hatcheries are...
- Published On: March 17, 2022
This project focuses on enhancing the food value chain for Tilapia in Region 3. Second to milkfish, tilapia is the most cultured freshwater fish in...
- Published On: March 17, 2022
The SKSU Agri-Aqua Technology Business Incubator will provide technical services to the incubatees for the promotion and commercialization of the developed technologies. The project will...
Capacity Building
Capacity building efforts of DOST-PCAARRD seek to develop and enhance the R&D capabilities of researchers and academic or research institutions through graduate assistantships, non-degree trainings & development, and/or upgrading of research facilities.
Infrastructure Development
Manpower Development
Policy Research & Advocacy
Analysis of policy concerns and advocacy of science-informed policies ensures that the AANR policy environment is conducive for S&T development and investments.

Competitiveness of Philippine Tilapia Industry under the ASEAN Economic Community
Tilapia production in the Philippines was found to be highly competitive in both export trade and import substitution scenarios. As long as the average tilapia yield, which is recorded to be 5.61mt/ha, does not drop to 2.22 mt/ha or domestic cost will not increase by 199%, sustaining the country’s Tilapia competitiveness is likely possible. However, further initiatives on increasing Tilapia yield in the Philippines would still be necessary to sustain and enhance the good performance of the industry.
Reference(s):
Manalo, N. Q. and Dorado, R. A. (2017). ASEAN Economic Community: Opportunities and Challenges for the Fishery Sector. Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: Philippine Council for Agriculture, Aquatic and Natural Resources Research and Development – (Project Report)
Market Advisory
Market advisories provide a variety of information, including selection of market outlets, emerging demand, technological advances, and potential business partners, among others.
- Published On: July 3, 2024
Explore Philippine fisheries' evolving landscape, influenced by market shifts, aquaculture growth, sovereignty issues amid escalating tensions over the West Philippine Sea,, floating solar project, and...
- Published On: April 11, 2024
Discover recent developments in the Philippine fisheries sector, including a notable rise in fish catch and substantial infrastructure investments. Image Source: The Philippine Star Increase...