Mussel
Industry Strategic Science and Technology Program
Mussel Industry Profile
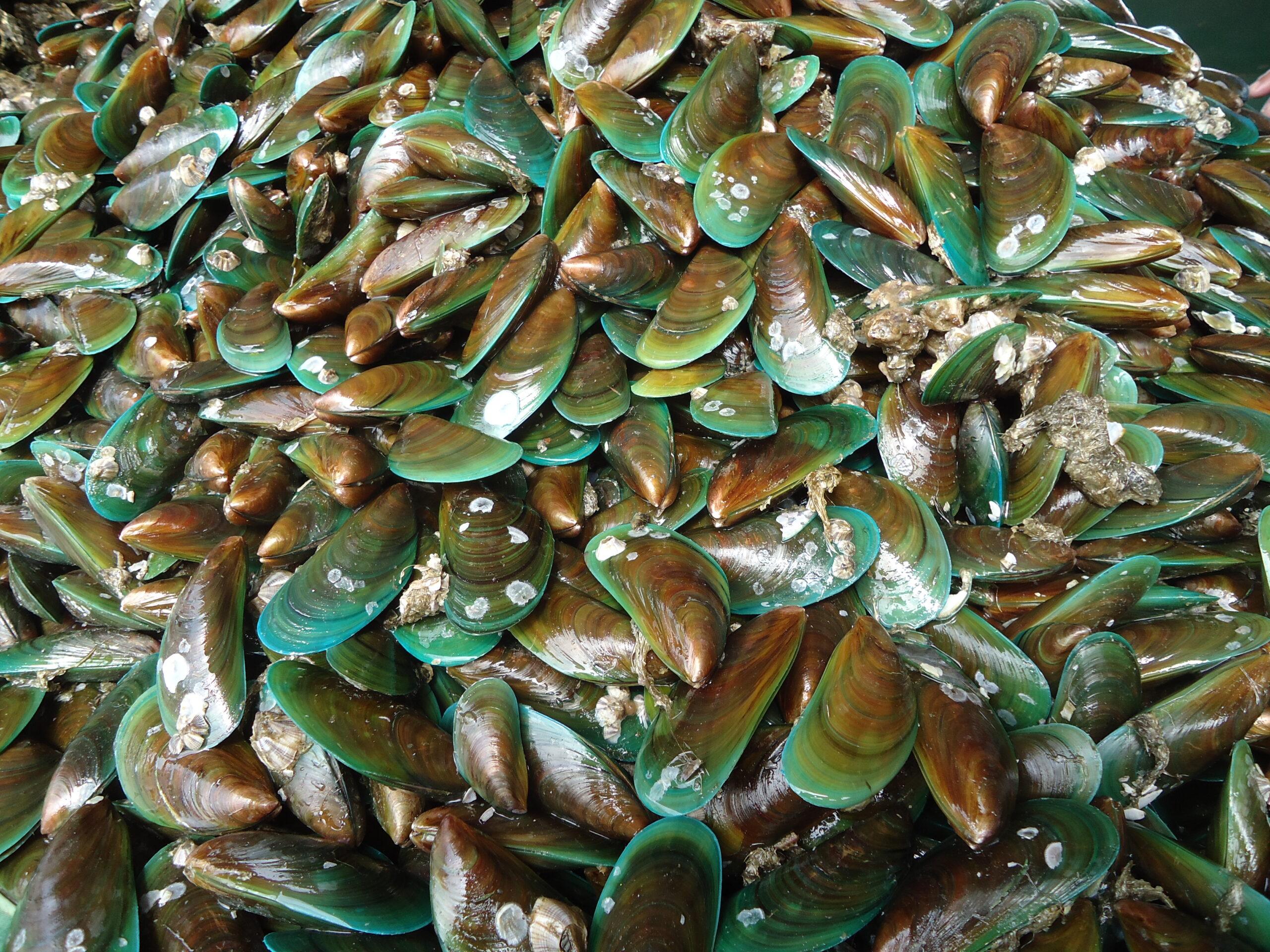
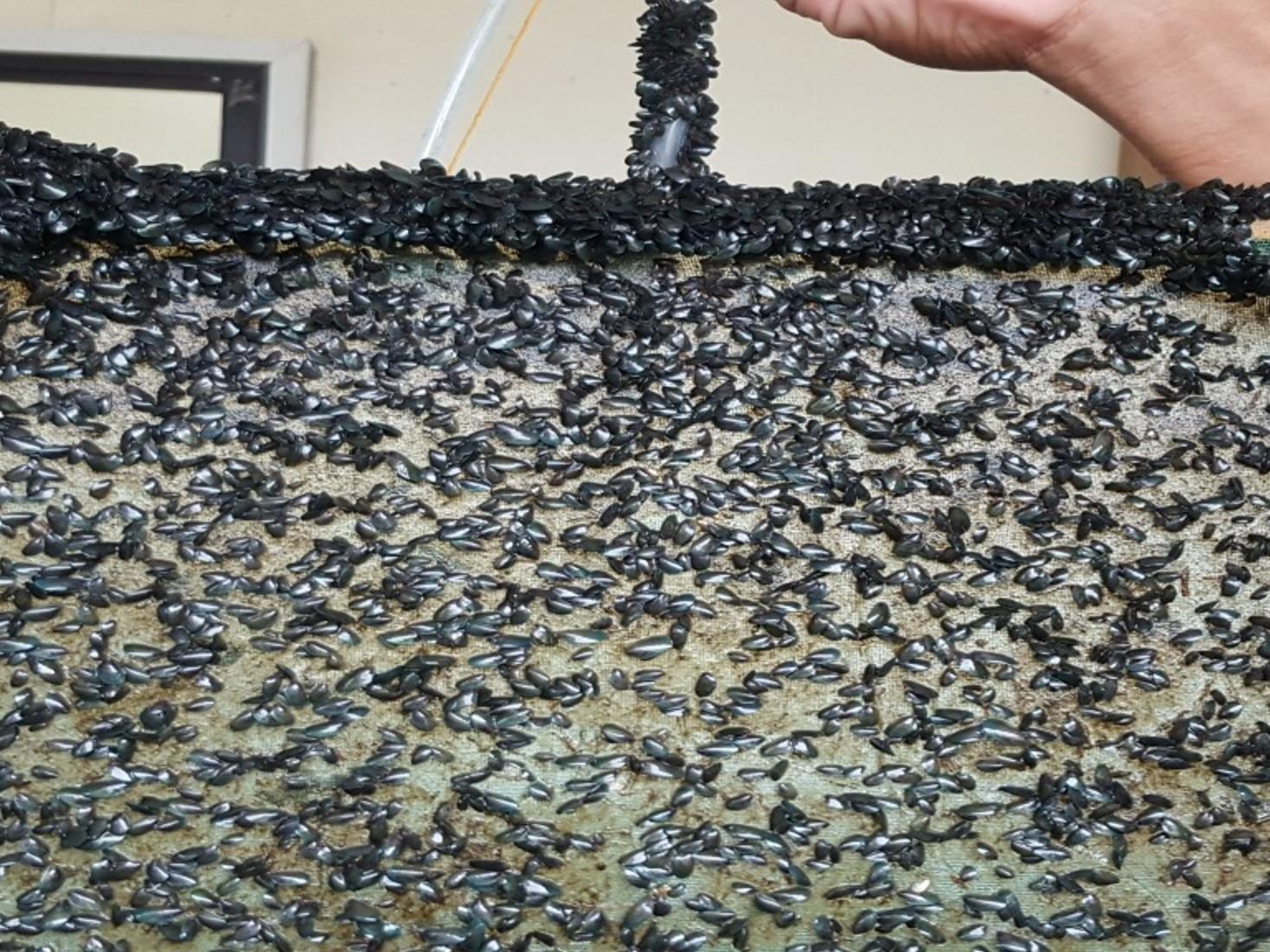
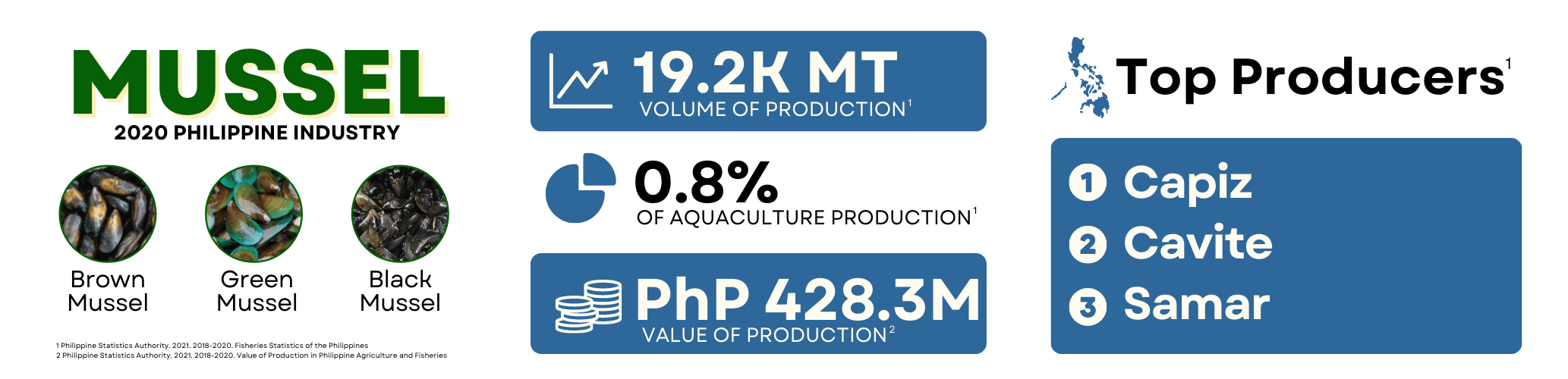
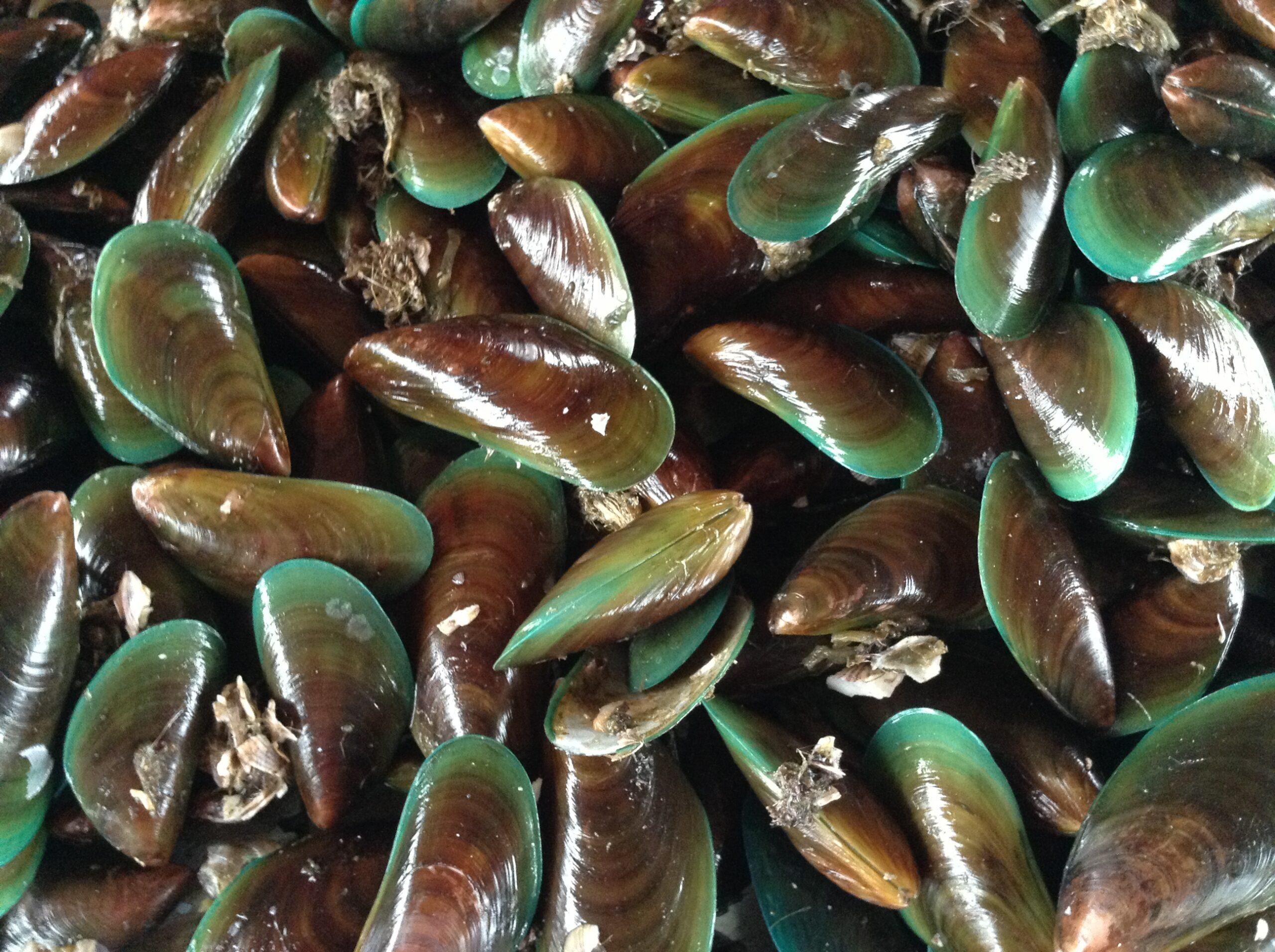
Mussels, locally known as “tahong”, are bivalve mollusks, meaning they have a two-part hinged shell as an external covering which contains a soft-boiled invertebrate. In the Philippines, the well-known species is the green mussel (Perna viridis). The mussel industry is an important component of the aquaculture sector in the Philippines as mussels are a cheap source of protein, and mussel farming provides additional income and livelihood to fisherfolk in many coastal areas as it only requires little capital investment. In 2020, PSA reported a total of 19,228.96 MT production for the Philippines. Western Visayas led the mussel production with 8,534.16 MT, of which 7,945.70 MT came from the province of Capiz. Other high producing provinces are Cavite and Samar with 5,654.23 MT and 4,077.14 MT, respectively.
Problems in the Industry
The production of farmed mussels decreased from 26,302.77 MT in 2018 to 19,229 MT in 2020. This can be traced to its low value and market demand due to the poor sanitary quality of produce and the occurrence of red tides. Furthermore, the area of its culture is limited by the existing stake culture method, which is restricted to shallow muddy areas, the crudeness of the spat transport method available, and the unpredictable supply of mussel seeds or spats. Other problems faced by the industry are inadequate supply of quality feeds and poor quality and unsafe mussel.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Data Source: Philippine Statistics Authority update as of May 30, 2024.
Mussel Policies
| Policy Type | Policy Number | Policy Year | Congress | Policy Title | Policy Description | Policy Objective | Policy Link | Commodity | Classification | info_encoder_stamp | info_date_stamp | info_quashing_remarks | filepath |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | House Resolution No. 2243 | 2021 | 18th | Resolution Urging The House Of Representatives Through The Committee On Aquaculture And Fisheries Resources To Conduct An Investigation, In Aid Of Legislation, On The Compliance Of Concerned Agencies To The Writ Of Continuing Mandamus For The Rehabilitation Of Manila Bay In Light Of The Recent Department Of Environment And Natural Resources (Denr) Order To Dismantle Mussel Farms And Fisheries Structures In Cavite | WHEREAS, on August 26, 2021, fisherfolk organization Pambansang Lakas ng Kilusang Mamamalakaya ng Pilipinas (PAMALAKAYA) issued a statement condemning the DENR order to dismantle the fishing and aquaculture structures in coastal towns of Cavite. According to PAMALAKAYA, the order would lead to the loss of livelihood of 15,000 fisherfolk and coastal residents in affected towns who directly depend on Manila Bay by culturing mussels and oysters. They added that the bamboo poles washed along the shore due to the monsoon were not pollutants harmful to the marine ecosystem like plastic and other solid wastes. They also pointed out that the structures caters to the food needs of thousands of residents along Manila Bay; WHEREAS, the PAMALAKAYA believes that the DENR order to dismantle the mussel farms in Cavite is a precursor to the massive reclamation plan in Cavite, such as the 420-hectare Bacoor Reclamation Project and the 1,331-hectare Cavite Five-Island Reclamation Project. The Bacoor Reclamation Project has already been granted an Environmental Compliance Certificate by the DENR since last year. Fisherfolk communities have been opposing the said reclamation project due to the threat of irreversible destruction not only on the livelihood of fisherfolk and coastal residents but also on Manila bay’s marine biodiversity and ecosystem; WHEREAS, according to reports gathered by PAMALAKAYA from affected fishing communities, small fisherfolk opposed the order but the strict lockdown in several barangays caused a delay in their protests against the said DENR order. On September 6, 2021, fisherfolk protested in front of the DENR Central Office to oppose the order to dismantle the mussel farms in Cavite. On September 7, fisherfolk and urban poor communities carried out a community protest to guard against the planned demolition of tahungan, talabahan, or any fisheries structures in the area. International food sovereignty groups such as the People’s Coalition on Food Sovereignty also supported the calls of Cavite fisherfolk and urban poor and carried out its online protest against the demolition order; | This resolution seeks to conduct an investigation, in aid of legislation, on the compliance of concerned agencies to the writ of continuing mandamus for the rehabilitation of Manila Bay in light of the recent DENR order to dismantle mussel farms and fisheries structures in Cavite. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_18/HR02243.pdf | Mussel | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Mussel_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Bill | House Bill No. 5789 | 2015 | 16th | An Act Establishing A Multi-Species Hatchery Under The Bureau Of Fisheries And Aquatic Resources For The Breeding And Production Of Bangus, Mudcrabs, Mussels, Oysters, Prawns And Similar Species In The Municipality Of Sultan Naga Dimaporo, Lanao Del Norte, To Be Known As The Lanao Del Norte Multi-Species Hatchery And Marine Science Center And Appropriating Funds Therefor | SECTION I . There shall be established, under the supervision of the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources of the Department of Agriculture, a multi-species hatchery for the breeding and production of bangus, mudcrabs, mussels, oysters, prawns and similar species in the Municipality of Sultan Naga Dimaporo, Lanao de! Norte to be known as the Lanao del Norte Multi-Species Hatchery and Marine Science Center. SECTION 2. The Lanao del Norte Multi-Species Hatchery and Marine Science Center shall conduct continuing research and experimentation of bangus, mudcrabs, mussels, oysters, prawns and similar species, as they apply to local conditions, to discover new methods and technology adaptive to prevailing weather conditions that will rejuvenate the aquaculture industry. SECTION 3. The Center shall disperse high-variety fry and fingerlings of said species in Panguil Bay, Iligan Bay and IIlana Bay in such periodic intervals as may be recommended by the Local Advisory Council established under the succeeding section. It may also sell such fry and fingerlings to individual or organized fish farmers at prevailing market prices. | This bill seeks to establish a multi-species hatchery in the Municipality of Sultan Naga Dimaporo, Province of Lanao del Norte to be known as the Lanao del Norte Multi-Species Hatchery and Marine Science Center marine science center. Its main objective is to breed and mass-produce fry and fingerlings for bangus, mudcrabs, mussels, oysters, prawns and marine species for dispersal in Panguil Bay, Jligan Bay and Iliana Bay. The Center shall be under the supervision of the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources of the Department of Agriculture. | https://docs.congress.hrep.online/legisdocs/basic_16/HB05789.pdf | Mussel | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Mussel_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Republic Act | Republic Act No. 9459 | 2007 | 13th | An Act To Establish An Oyster, Mussel, Crab, Prawn And Shrimp Farm In The Municipality Of Calabanga, Province Of Camarines Sur, Appropriating Funds Therefor And For Other Purposes | SEC 3. The Department of Agriculture, through the oyster, mussel, crab, prawn and shrimp farm, is hereby authorized to conduct such researches and experiments as may be necessary to improve existing technology on oyster, mussel, crab, prawn and shrimp and such other marine and aquatic animals farming and to enhance and maximize income potentials of said industry. The Department shall assist the local government to establish, in appropriate locations, their own oyster, mussel, crab, prawn and shrimp farms as pilot demonstration farms or as economic enterprises for local revenue generating purposes. SEC 4. The Secretary of Agriculture shall include in the Department’s program the funding requirements for the establishment and operationalization of the oyster, mussel, crab, prawn and shrimp farm in the Municipality of Calabanga, Province of Camarines Sur. Thereafter, such sum as may be necessary for its continued operation and maintenance shall be included in the annual General Appropriations Act. | This aims to establish an oyster, mussel, crab, prawn and shrimp farm in the Municipality of Calabanga, Province of Camarines Sur, which shall be udner the supervision and control of the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources of the Department of Agriculture. | https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/2007/05/15/republic-act-no-9459/ | Mussel | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Mussel_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx | |
| Order | Fisheries Administrative Order No. 138 | 1982 | Null | Rules and regulations governing the culture of mussels (tahong) | SEC. 2. Prohibition. - No person, association, corporation, partnership or cooperative shall culture mussels without a license duly issued by the Director | This order aims to provide the rules and regulations on the culture of mussels | https://www.bfar.da.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/FAO-No.-138-s.-1982.pdf | Mussel | Null | Jeff | 11/22/2024 | C:\Users\trist\Documents\Formatting\Output\Mussel_2024-11-22_processed.xlsx |
ISP for Mussel
The PCAARRD Industry Strategic S&T Program for mussel aims to help develop the mussel industry by enabling farmers to produce quality and safe cultured and processed mussel products. It will develop technologies to provide farmers with a sustainable and reliable source of quality mussel seeds and enable the expansion of production areas for mussel farming.
Strategic R&D
Strategic R&D is DOST-PCAARRD’s banner program comprising all R&D activities that are intended to generate outputs geared towards maximum economic and social benefits
Mussel Biotechnology Program developed high-value compounds such as shelf-stable bioactive peptides, encapsulated lipid products, and food-grade and lab-grade glycogen from mussels. Promising results include qualification...
The project determined the distribution of Mytella strigata in Philippine waters, the impacts of these species on mussel growers, how local government units respond to...
As the LGU of Bacoor is planning to integrate the mussel industry into their tourism plan and highlight their effort on producing safe and quality...
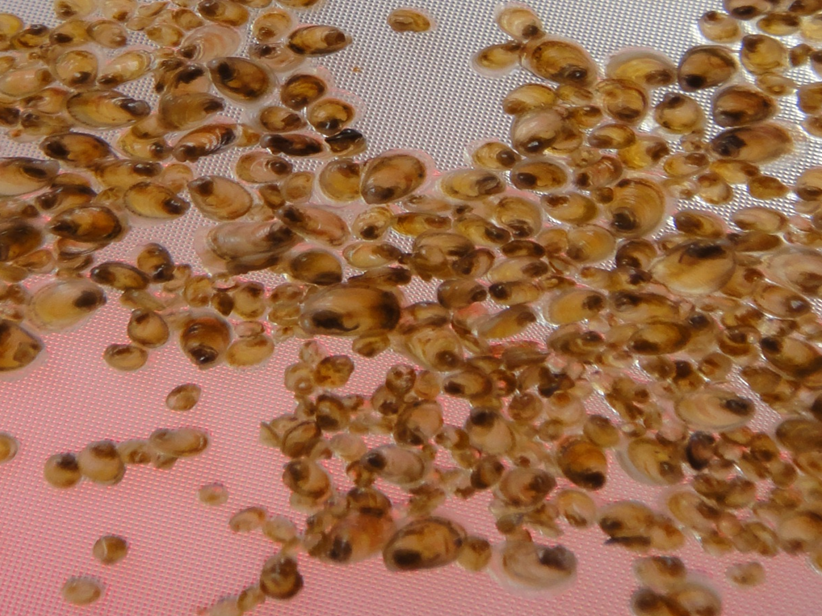
This project improved the production of green mussel spat needed for grow-out. Viable spawning technique using thermal stimulation and desiccation was proven effective for the...
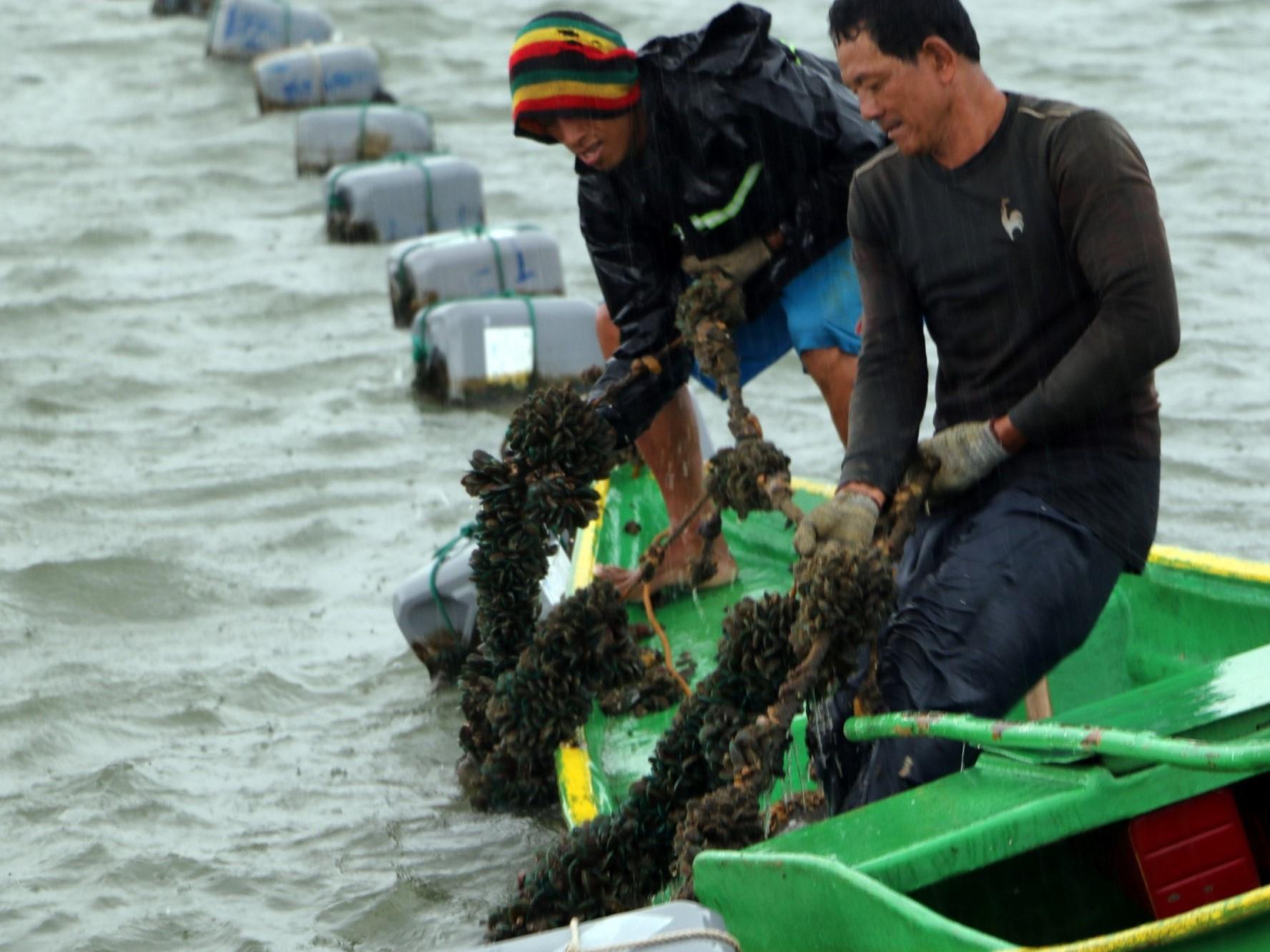
Mussel longline method was tested for its efficiency and profitability in different study sites to verify and compare the environmental effect from the stake method....
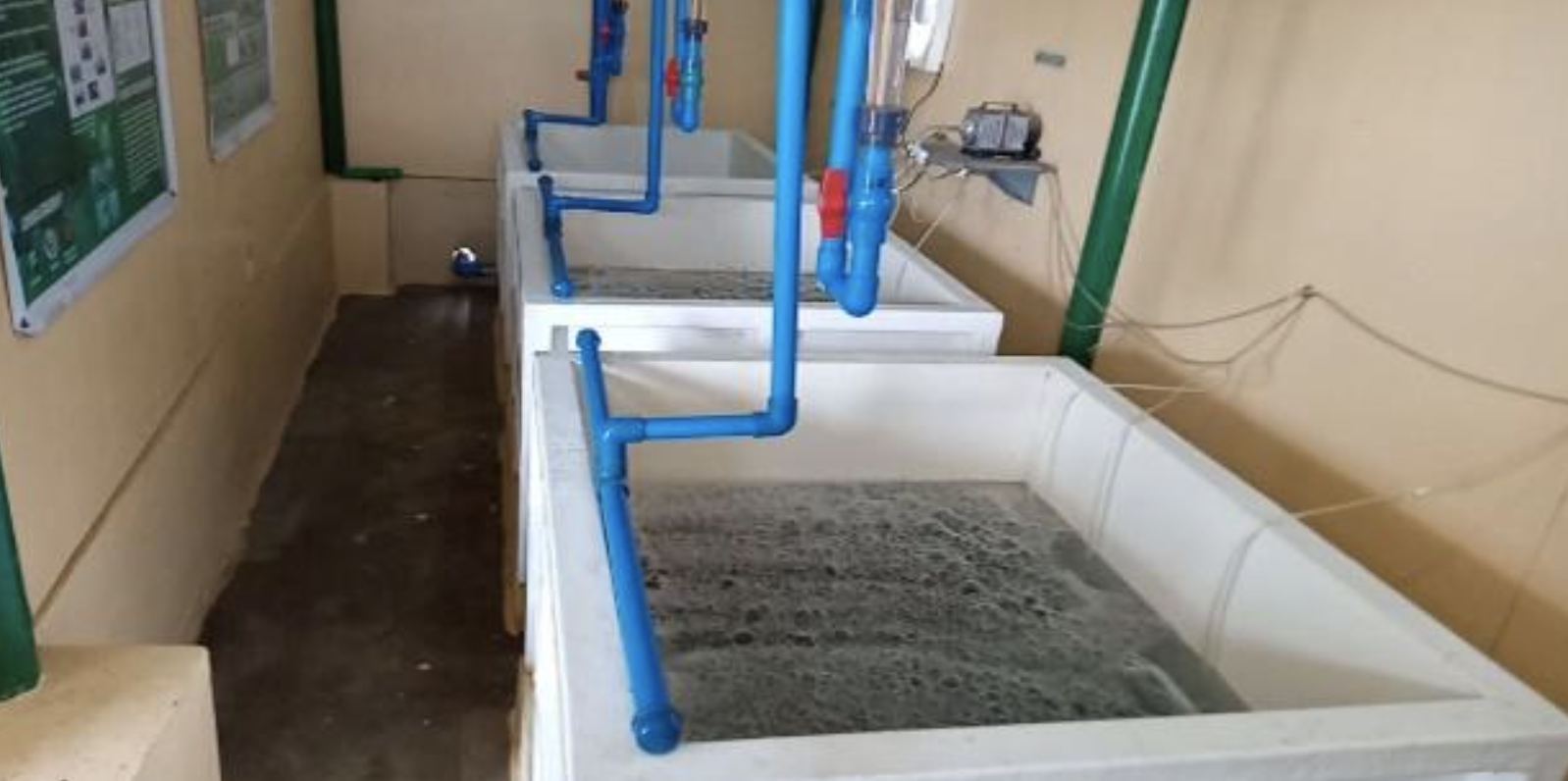
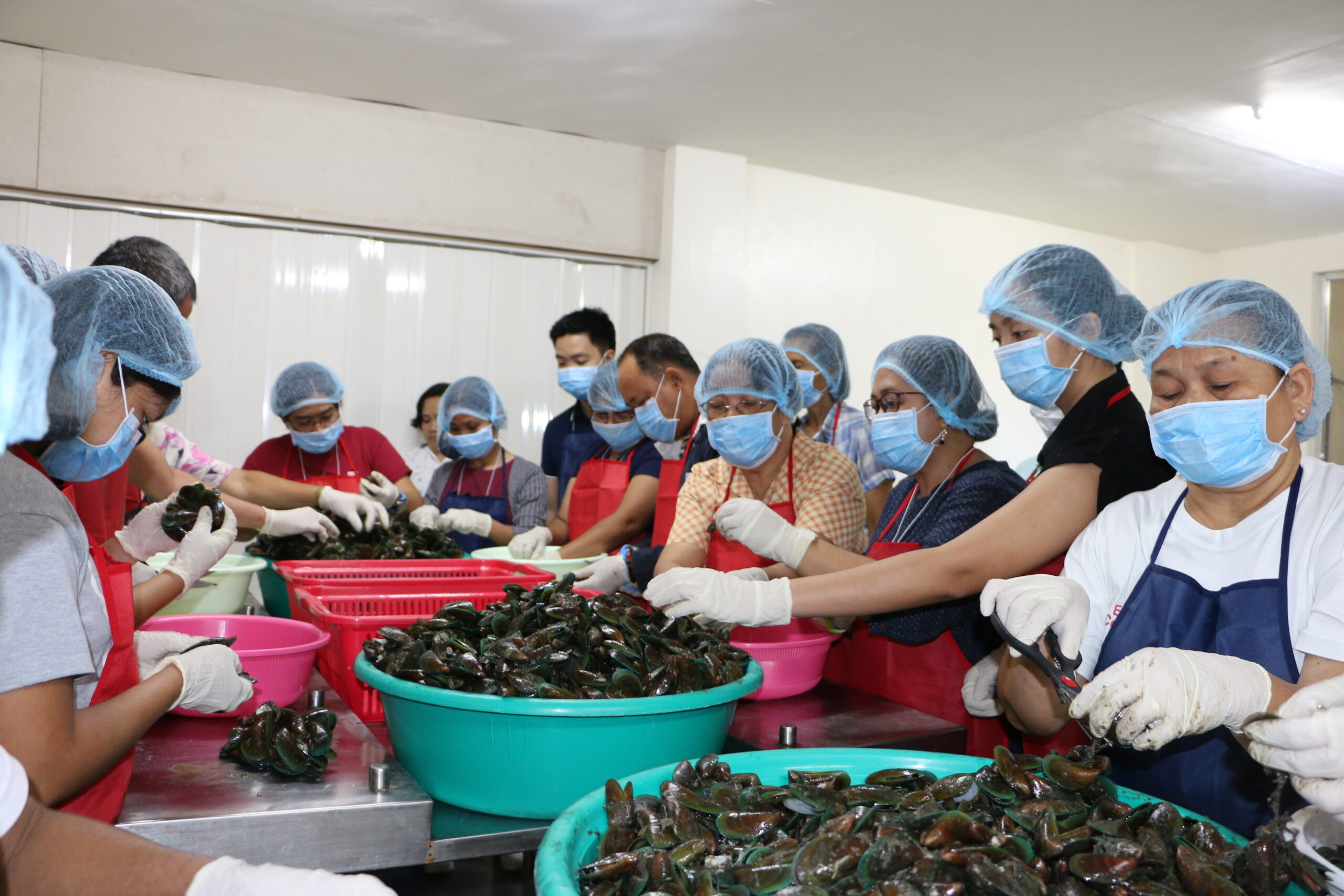
This project verified the developed technologies, such as low temperature live handling, blanching, and acid pre-treatment to produce chilled and frozen mussels, to come up...
Value-added products from mussel are also currently available in the local market such as dried mussel crackling, fermented mussel paste (bagoong), bottled smoked mussel, and...
To provide an adequate response to the problem of low production in the mussel industry, it is important to utilize possible sites where both hydrographic...
This project is a spin-off of the previous project titled "Development of depuration and relaying techniques for Philippine green mussels". Depuration and relaying are effective...
Verification of longline technology at different productivity and depth would aid in the expansion of culture areas in the country. The longline system is more...
Project 1. Development of depuration and relaying techniques for Philippine green mussels (Perna viridis) Project 2. Primary processing techniques for Philippine green mussels Project 3. Evaluation of...
Project 1. Transplantation and spatfall determination of green mussel, Perna viridisProject 2. Raft and long-line culture of the green mussel, Perna viridisProject 3. Causes and...
Project 1. Refinement of broodstock maintenance, spawning, larval and spat rearing technologies for sustained seed production of the green mussel (Perna viridis) Project 2. Development...
Technologies
Products, equipment, and protocols or process innovations developed to improve productivity, efficiency, quality, and profitability in the agriculture and aquatic industries, and to achieve sustainable utilization and management of natural resources
- Published On: March 17, 2022
Pre-processing is necessary to bring quality and safe mussels to the consumers. Depuration is a process of eliminating or reducing bacterial load in mussels by...
- Published On: March 17, 2022
Mussel Longline Technology is an alternative to stake method in culturing mussels. It consists of a mainline of at least 18-millimeter (mm) diameter polypropylene (PP)...
- Published On: March 17, 2022
One major problem that hinders the sustainability of mussel production is the reliance of the industry on seed stock from the wild. The natural population...
Capacity Building
Capacity building efforts of DOST-PCAARRD seek to develop and enhance the R&D capabilities of researchers and academic or research institutions through graduate assistantships, non-degree trainings & development, and/or upgrading of research facilities.
Infrastructure Development
Manpower Development
Policy Research & Advocacy
Analysis of policy concerns and advocacy of science-informed policies ensures that the AANR policy environment is conducive for S&T development and investments.

Competitiveness of Philippine Mussel Industry under the ASEAN Economic Community
The study shows that stake, longline and raft mussels, are competitive in the export trade and import substitution scenarios. Stake, longline and raft mussels are competitive internationally and have the potential to earn foreign exchange as export commodities. Concurrently, the local production costs of these mussel varieties are relatively cheaper, therefore can compete with imported commodities.
Reference(s):
Andal, E. G., Lapiña, G. F., Manalo, N. Q., Dorado, R. A. Valientes, R. M., & Cruz, M. B. (2017). ASEAN Economic Community: Opportunities and Challenges for the Agriculture, Fishery, and Forestry Sectors. Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines: Philippine Council for Agriculture, Aquatic and Natural Resources Research and Development – (Project Report)